How To Calculate Force With Pressure And Area

1.2.2 Determine Force and Center of Pressure on Triangular Gate Example 2 YouTube
Draw the triangle and circle the required property. To calculate the pressure we would need to divide the force by the area. Substitute values for the other two properties and complete the calculation. A=200m^ {2}, 800\div {200}=4. Write down the solution, including the units. = 4 \ N / {m^ {2}}=4 \ Pa.

Relation between Pressure, Force and Area Part2 Animated Science Video elearn K12 YouTube
3 Answers Sorted by: 1 You can prove it by noticing all the forces acting on your system. If your system is the triangle plus the weights, then there are two forces acting, gravity (downwards) and the force from the person.

Force Area Pressure Formula Cazoom Maths Worksheets
Beyond's simple to use Pressure Force Area Triangle Desk Prompt helps GCSE Physics students calculate force, pressure and area. The prompts also provide help to students with rearranging the equations. Take the pressure off GCSE Physics with Beyond.

Mechanical Minds DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FORCE AND PRESSURE EXPLAINED
Pressure, force, area formula triangle This equation tells us that: If a force is spread over a large area it will result in a small pressure If it is spread over a small area it will result in a large pressure High heels produce a higher pressure on the ground because of their smaller area, compared to flat shoes Did this video help you?
Pressure Force Area GCSE Maths Steps& Examples
What force is exerted at 90° to the area? First rearrange the equation to find force normal to surface area: force normal to a surface area = pressure × area of that surface Next.

View Source
Then, the force exerted on the plate is simply the weight of the water above it, which is given by. F = ρAs, where ρ is the volumetric density of water. To find the hydrostatic pressure - that is, the pressure exerted by water on a submerged object - we substitute F from Equation 1.6.2 into Equation 1.6.1 so that.
PPT EDEXCEL IGCSE / CERTIFICATE IN PHYSICS 51 Density and Pressure PowerPoint Presentation
The Corbettmaths Practice Questions on Pressure. Videos, worksheets, 5-a-day and much more

Pressure Force Area Triangle Physics Stock Vector (Royalty Free) 2128084781 Shutterstock
E. Elliott Whipps. Pressure = Force / Area. Pressure is measured in Pascals (Pa), Force is measured in Newtons (N) and Area is measured in metres squared (m^2). To find the pressure exerted on a surface, ensure your units are correct (i.e. make sure force is in Newtons, not nano-newtons for example!) and then divide Force by Area.
Basic Biomechanics Pressure
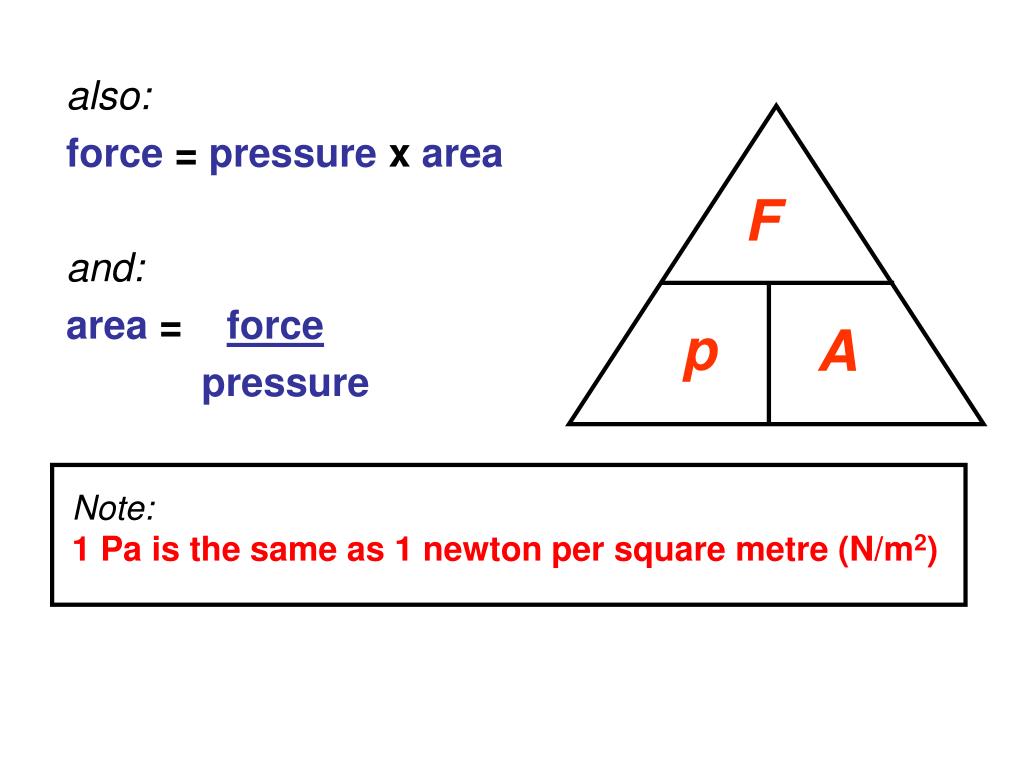
F is force (N) A is area (m 2) Pressure is measured in the units Pascals (Pa) The area should always be the cross-sectional area of the object This means the area where the force is at right angles to it This equation can be rearranged with the help of a formula triangle: Formula Triangle for Pressure Pressure, force, area formula triangle
PPT Pressure = Force/Area PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4710715
The second formula that we need is the following. Assume that a constant pressure P P is acting on a surface with area A A. Then the hydrostatic force that acts on the area is, F = P A F = P A. Note that we won't be able to find the hydrostatic force on a vertical plate using this formula since the pressure will vary with depth and hence will.
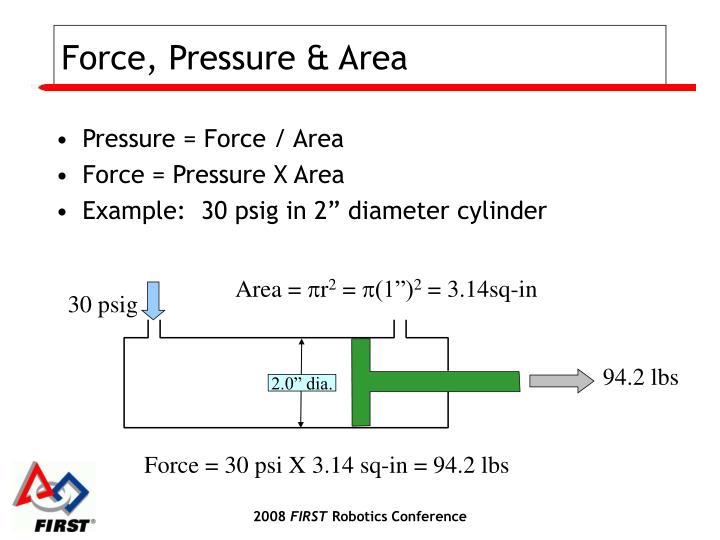
PPT Pneumatic Power PowerPoint Presentation ID1204607
Pressure Triangle - Pressure = Force / Area Pressure is how much force there is per unit of area. Common units for this are N/m 2 (the proper name for this is Pascals (PA)). Example - Calculate the total force applied on a surface of 0.5 m 2 where the average pressure is 1.5 N/cm 2. First convert the units so they match.

HTPIB13C Pressure, Force, Area YouTube
The total force on a submerged vertical or inclined plane surface is equal to the area of the surface times the depth of the centroid. Example 16.5.1 16.5. 1. Figure XVI.6 shows a triangular area. The uppermost side of the triangle is parallel to the surface at a depth z z. The depth of the centroid is z + 13h z + 1 3 h, so the pressure at the.
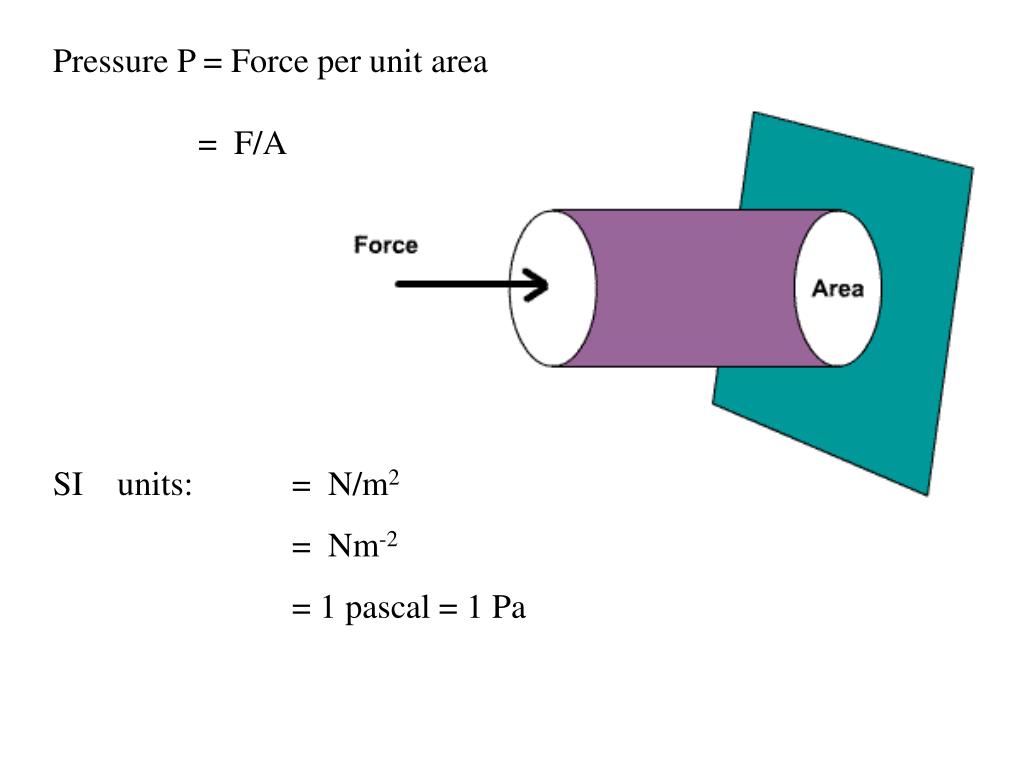
PPT Pressure P = Force per unit area = F/A SI units = N/m 2 PowerPoint Presentation ID2617419
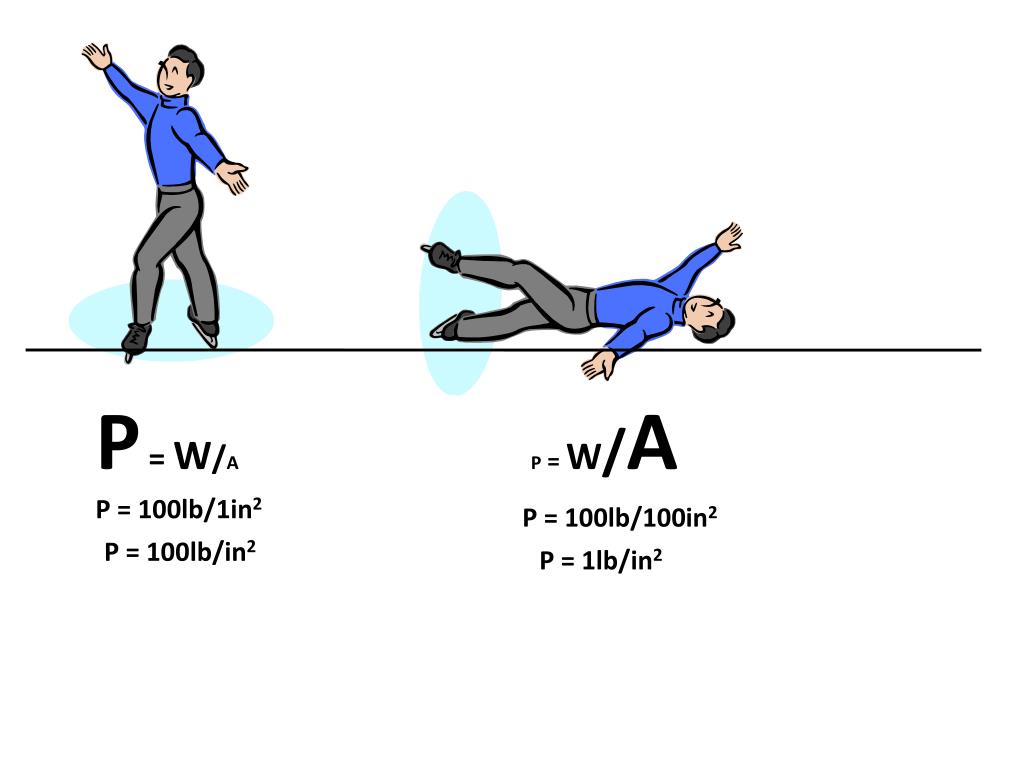
Effects of force and area on pressure A rock resting on a soft surface, like sand or mud, will create an indentation. The depth of this indentation depends on the pressure exerted on the.

Cylinder Force Factors Clippard Pressure Force Area Dot Png,White Triangle Png free
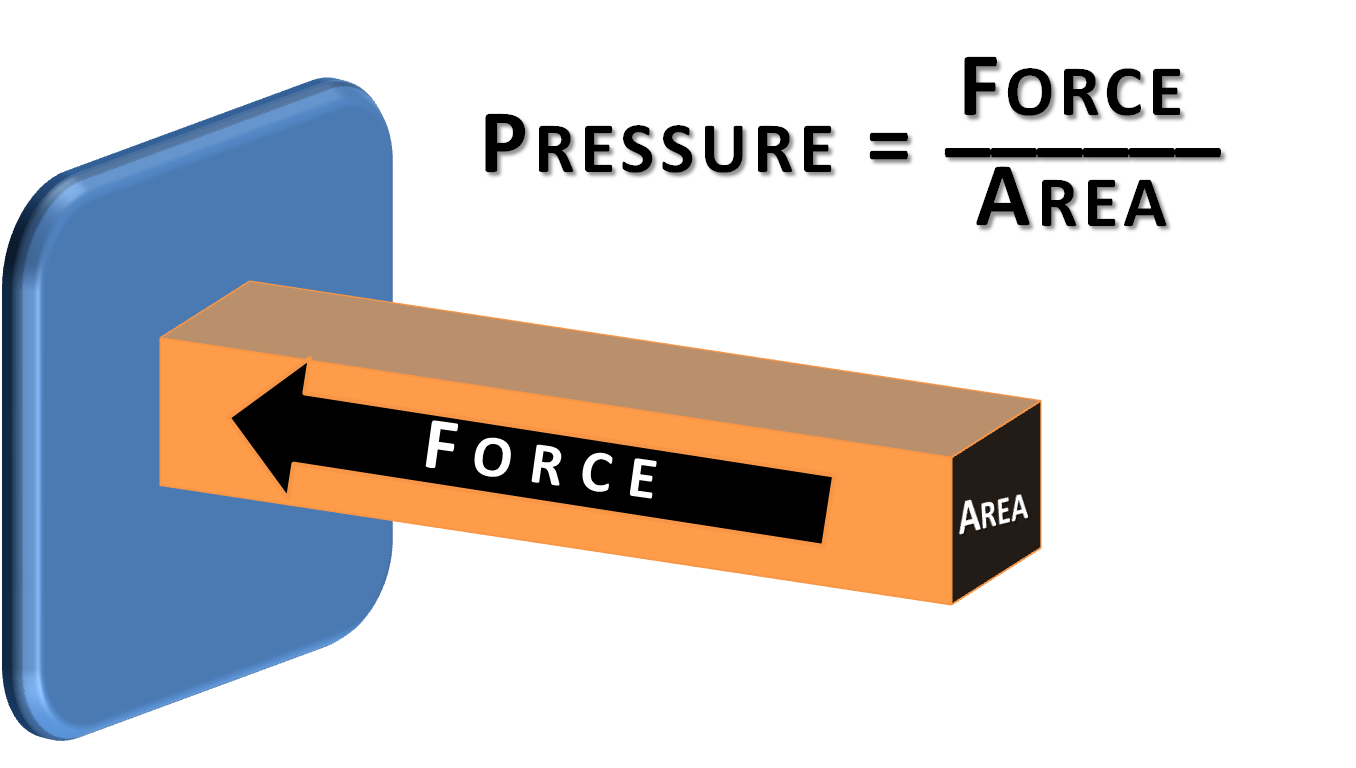
Pressure is calculated by dividing the amount of force by the area. The pressure formula (or pressure equation) is therefore \text {pressure}=\frac {\text {force}} {\text {area}}\text { or }P=\frac {F} {A} pressure = areaforce or P = AF. Pressure is a compound measure made from force and area. Pressure equals the force per unit area.
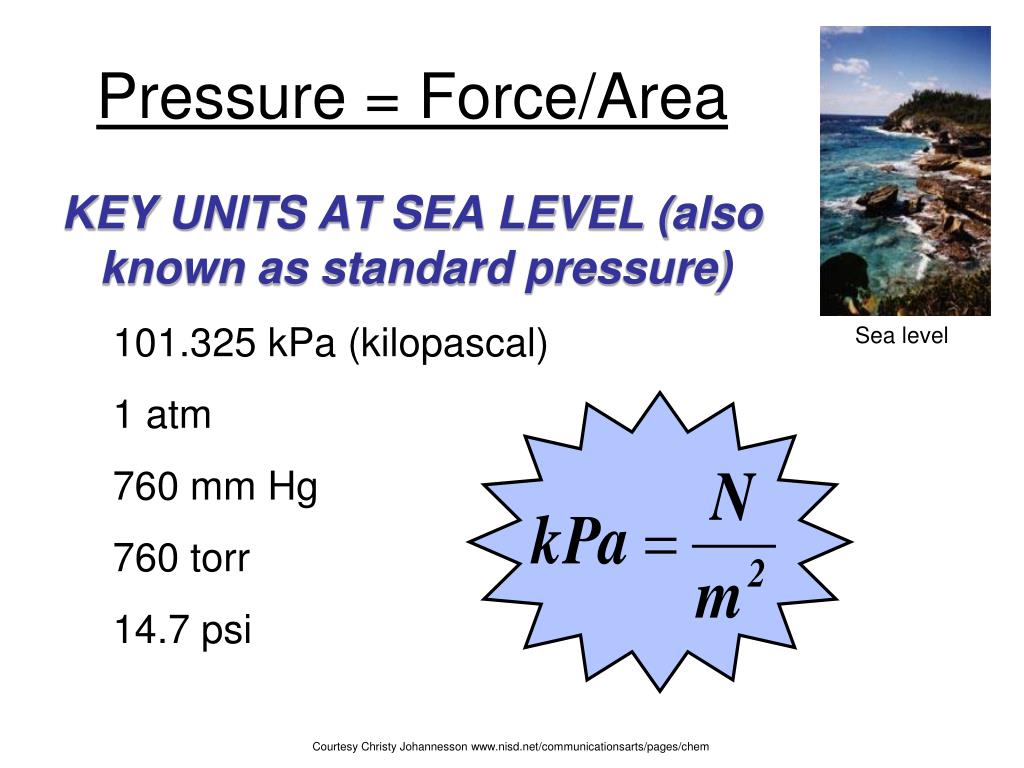
PPT Properties of Gases PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6015649
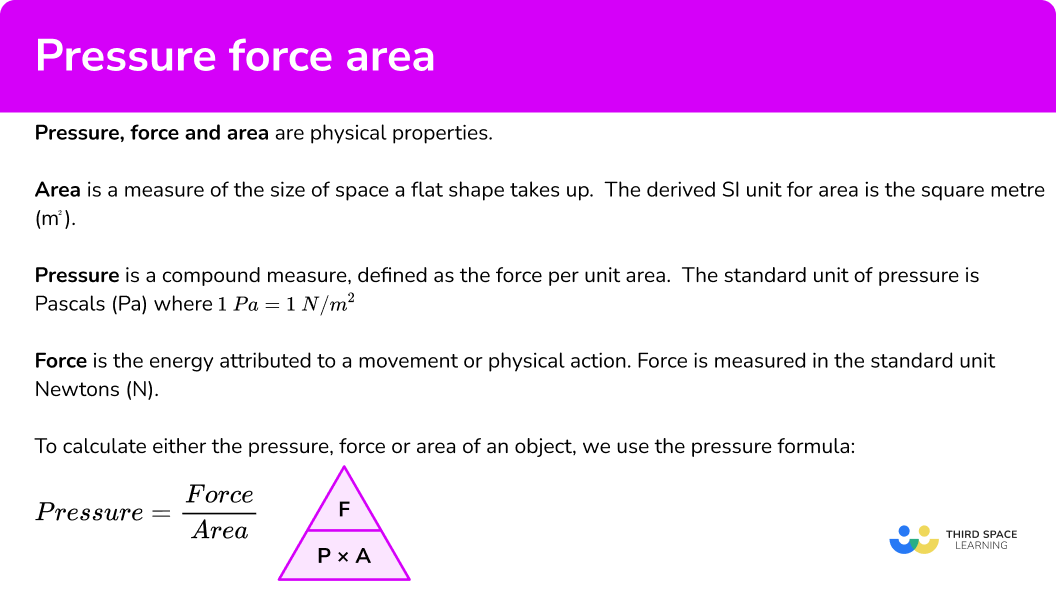
Pressure, force and area are all related by the formula: p = \dfrac {F} {A} where p is the pressure, F is force, and A is area. You can rearrange this formula to find the other two, for example, if we multiply both sides of the equation by A, then swap the left-hand side and right-hand side, we get. F = p \times A

Pressure, Force and Area Simple physics tutorial (GCSE) YouTube
Frequently Asked Questions What is the formula for pressure, force, and area? Pressure is defined as force per unit area. It is expressed as P = F/A, where P is pressure in pascals, F.