subdural hematoma vs epidural hematoma XRAY Google Search Neuro Pinterest Grey, Old
Anatomy Epidural vs Subdural Hematoma Image
For more video tutorials, high-yield revision Qbanks and support from our online Community, Sign Up at https://www.surgicalteaching.com. Use Coupon code STYo.

Subdural Hematoma Vs Epidural Hematoma slidesharetrick
A subdural hematoma is a type of brain bleed. Blood leaks out of a blood vessel into the space below the outermost membrane of the brain -- the dura mater. What is a subdural hematoma? A subdural hematoma is a type of bleed inside your head. It's a type of bleed that occurs within your skull but outside the actual brain tissue.

Clinics in neurology and neurosurgeryextradural and subdural haematoma Davis et al. 44 (16
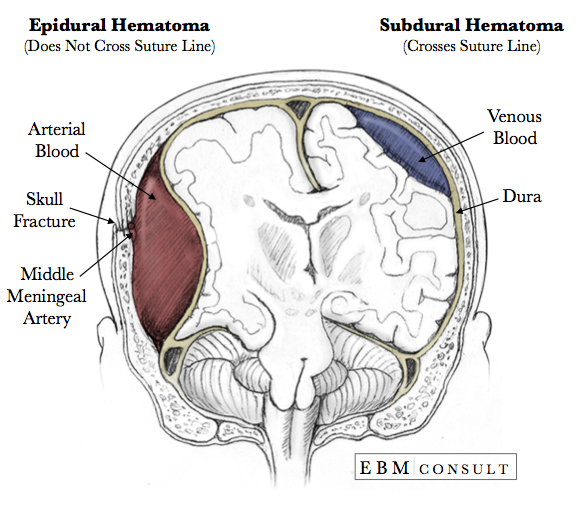
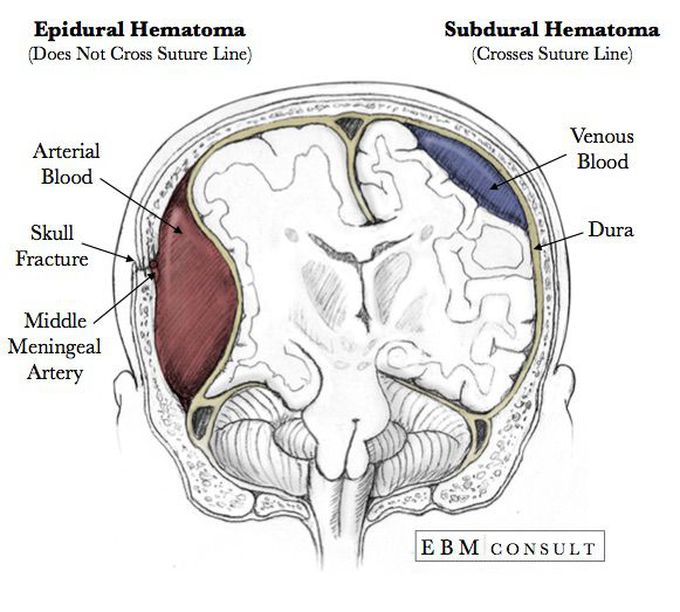
Subdural hematomas are interposed between the dura and arachnoid. Typically crescent-shaped, they are usually more extensive than extradural hematomas. In contrast to extradural hemorrhage, subdural hemorrhage is not limited by sutures but is limited by dural reflections, such as the falx cerebri, tentorium, and falx cerebelli.
Epidural Hematoma vs. Subdural Hematoma MEDizzy
A subdural hematoma occurs when a blood vessel near the surface of the brain bursts. Blood builds up between the brain and the brain's tough outer lining. The condition is also called a subdural hemorrhage. In a subdural hematoma, blood collects immediately beneath the dura mater. The dura mater is the outermost layer of the meninges.

SUBDURAL VS EPIDURAL HEMATOMA RADIOLOGY Wroc?awski Informator Wroc?aw, Wroclaw
Extradural haematoma (EDH) is defined as an acute haemorrhage between the dura mater and the inner surface of the skull. An EDH can cause compression of local brain structures and a rise in intracranial pressure. If intracranial pressure continues to rise, cerebellar herniation may occur leading to brainstem death.

EPIDURAL & SUBDURAL HEMATOMA Medical Facts, Medical Science, Computer Science, Icu Nursing
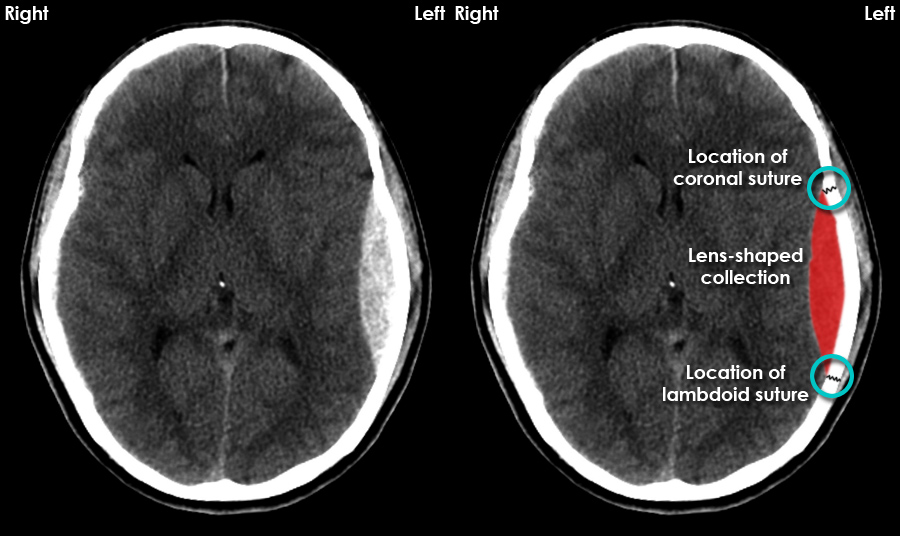
See the article: extradural hemorrhage vs subdural hemorrhage. Pathology. The source of bleeding is typically from a torn meningeal artery, usually the middle meningeal artery (75% 7). An associated skull fracture is present in ~75% of cases 3. Pain (often severe headache) is caused by the stripping of dura from the bone by the expanding.

Anatomy Epidural vs. Subdural Hematoma Medicine Notes, Medicine Studies, Brain Anatomy, Anatomy
Epidural hematomas (EDHs) and subdural hematomas (SDHs), or so-called extra-axial bleedings, are common clinical entities after a traumatic brain injury (TBI), and both are often present in the same subject [ 1 ].

Pin on Medicina
SDH is a collection of blood between the dural and arachnoid coverings of the brain. As the volume of the hematoma increases, brain parenchyma is compressed and displaced, and the intracranial pressure may rise and cause herniation. While the presence of SDH can be inferred by neurologic decline and mechanism of traumatic injury, the diagnosis.

Head injury in adults Induction RCEMLearning India
Overview An intracranial hematoma is a collection of blood within the skull. It's usually caused by a blood vessel that bursts in the brain. It may also be caused by trauma such as a car accident or fall. The blood may collect in the brain tissue or underneath the skull, pressing on the brain.
Acute CT Brain Extraaxial haemorrhage
Duret hemorrhages are associated with descending transtentorial herniation, which can occur due to various underlying causes. Herniation syndromes manifest as a result of increased intracranial pressure, leading to shifts in intracranial compartments. The etiology of Duret hemorrhages include 8: epidural hemorrhage. subdural hemorrhage.

Subdural Hematoma Neurology Medbullets Step 2/3
Extradural Hematoma vs. Subdural Hematoma. A hematoma is a medical term for a blood clot, formed when bleeding occurs in an organ or cavity. Extradural hematoma or epidural hematoma (EDH) is a clot that forms on the external side of the brain's protective layer of tissue (dura mater), whereas acute subdural hematoma (ASDH) appears within the first few days after head injury, on the interior.
Extradural vs Subdural Haematomas How do we Diagnose them on CT? YouTube
A subdural hematoma describes a type of bleeding that causes irritation and pressure in the brain. It is sometimes also called a subdural hemorrhage. Subdural hematomas happen in a region called the subdural space. The subdural space is the area between the surface of the brain and the dura, a layer of protective tissue located between the.

Download Subdural vs Epidural Hematoma/Hemorrhage [CT Scan Findings] Watch online
An epidural hematoma (EDH) is a collection of blood that forms between your skull and the dura mater, the outermost protective membrane covering your brain. The cause is usually an artery that gets torn by a skull fracture. Symptoms include severe headache and loss of consciousness.

subdural hematoma vs epidural hematoma XRAY Google Search Neuro Pinterest Grey, Old
Both extradural and acute subdural haematoma are serious conditions that can cause compression of the underlying brain, and usually are a result of significant head trauma, which may be associated with a brief episode of loss of consciousness. Causes Extradural haematoma (usually from a torn artery in the skull)… Head trauma. Fracture of skull.

Epidural Vs Subdural Hematoma Mnemonic Diagram Of Subdural Hematoma Gambaran
A venous epidural hematoma occurs when there is a skull fracture, and the venous bleeding from the skull fracture fills the epidural space. Venous epidural hematomas are common in pediatric patients. Subdural Hematoma Subdural hemorrhage occurs when blood enters the subdural space which is anatomically the arachnoid space.

Subdural Hematoma Vs Epidural Hematoma slidesharetrick
An extradural haematoma (also termed an epidural haematoma) is an extra-axial bleed occurring between the dura and skull bone. Around 2% of all head injuries presenting to the emergency department are extradural haematomas (EDHs), with associated significant morbidity and mortality, especially with advancing age.