(PDF) Linear mixed effects modeling in SPSS · Linear mixedeffects
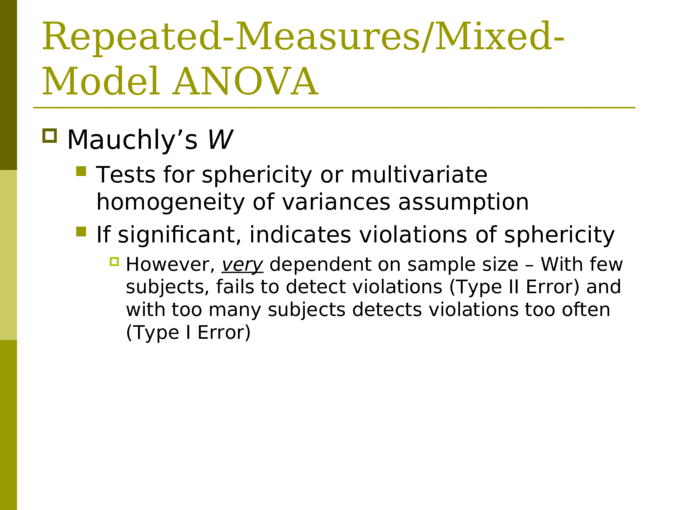
Repeated Measures/Mixed Model ANOVA SPSS Lab 4. [PPT Powerpoint]
The next most frequently used software was SPSS (8%; IBM IBM Corp, 2013).. (repeated measures) anova"). However, mixed-effects models were also found to be more conservative, depending on how the random effects structures were specified (8%; e.g., "Mixed models are typically more conservative, but not always"). Traditional F1/F2 tests.

How to do Generalized linear mixed model in SPSS by Gemechu Fufa YouTube
In this article we document for posterity how to fit some basic mixed-effect models in R using the lme4 and nlme packages, and how to replicate the results in SPSS. In this article we work with R 4.2.0, lme4 version 1.1-29, nlme version 3.1-157, and SPSS version 28.0.1.1.
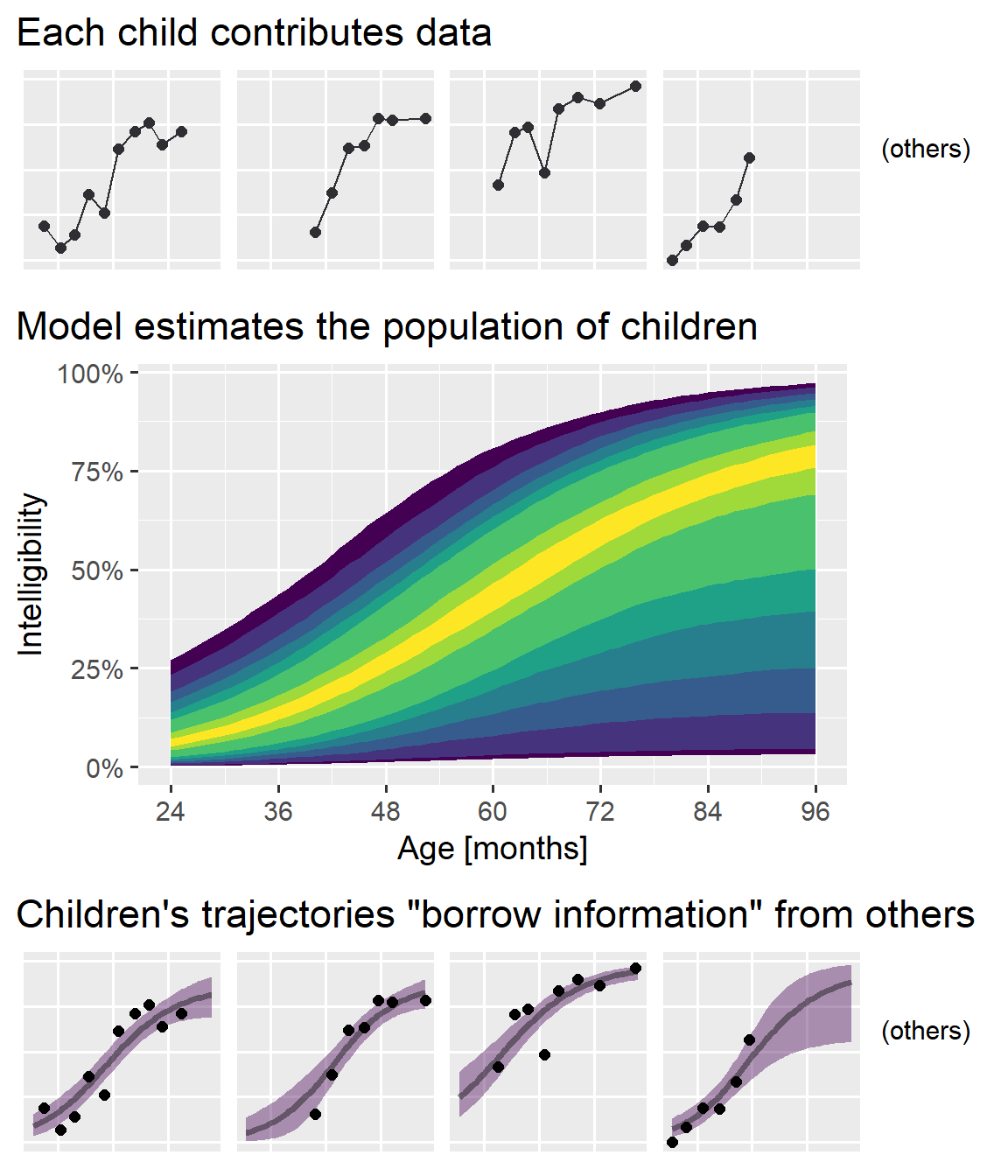
Another mixed effects model visualization Higher Order Functions
Mixed effects models refer to a variety of models which have as a key feature both fixed and random effects. The distinction between fixed and random effects is a murky one. As pointed out by Gelman (2005), there are several, often conflicting, definitions of fixed effects as well as definitions of random effects.

Mixed Models in SPSS and interpretation of Random Effects Cross Validated
Analysing repeated measures with Linear Mixed Models (random effects models) (1) Robin Beaumont [email protected] D:\web_sites_mine\HIcourseweb new\stats\statistics2\repeated_measures_1_spss_lmm_intro.docx page 4 of 18 2. Wide and long data formats
SPSS Mixed Command
My answer: No. (And by the way, this is all true in SAS as well. I'll include the SAS versions in parentheses). You can think of SPSS Mixed (SAS proc mixed) as the clustered-data version of SPSS GLM (proc glm). They have a lot of similarities in both their syntax and the kinds of models they can run.
Modern repeated measures analysis using mixed models in SPSS (2) YouTube
Repeated measures analyse an introduction to the Mixed models (random effects) option in SPSS. Demonstrates different Covariance matrix types & how to use.
SPSS Mixed Command
Linear Mixed Models is used to estimate the effect of different coupons on spending while adjusting for correlation due to repeated observations on each subject over the 10 weeks. Methods Maximum likelihood (ML) and restricted maximum likelihood (REML) estimation. Statistics
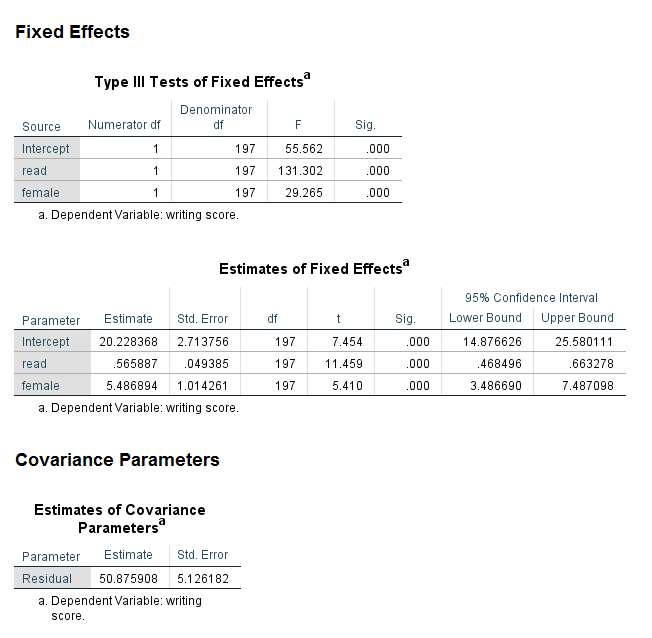
DSA SPSS Short Course Module 9 Linear Mixed Effects Modeling
The mixed command in SPSS is used to run linear regression models, including mixed effects models. When most people think of linear regression, they think of ordinary least squares (OLS) regression. In this type of regression, the outcome variable is continuous, and the predictor variables can be continuous, categorical, or both.

Repeated Measures/Mixed Model ANOVA SPSS Lab 4. [PPT Powerpoint]
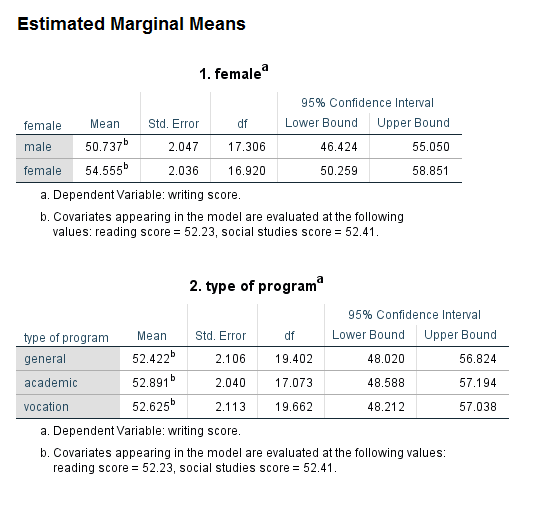
At the end of the experiment, the psychologist uses a mixed ANOVA to determine whether any change in depression (i.e., the dependent variable) is the result of the interaction between exercise intensity (i.e., the "conditions/treatments", which is the within-subjects factor) and gender (i.e., a "characteristic" of the sample, which acts as the b.

Modern repeated measures analysis using mixed models in SPSS (1) YouTube
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright.
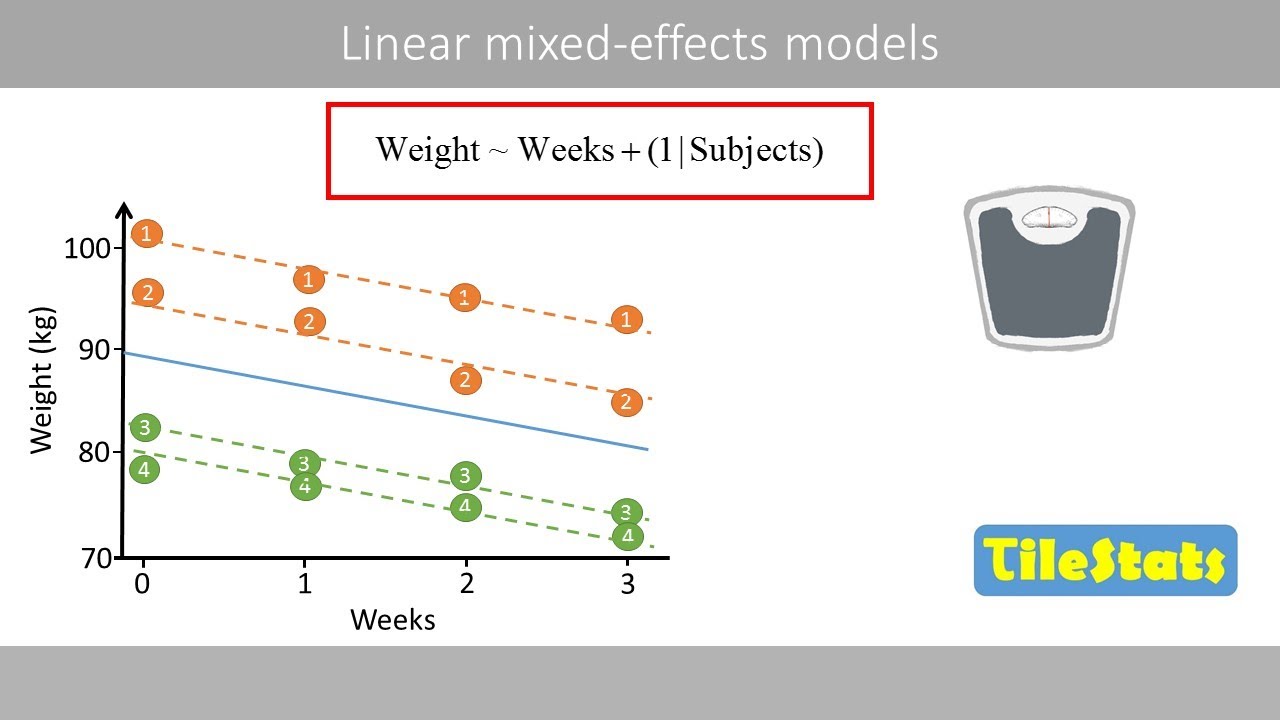
Linear mixed effects models random slopes and interactions R and
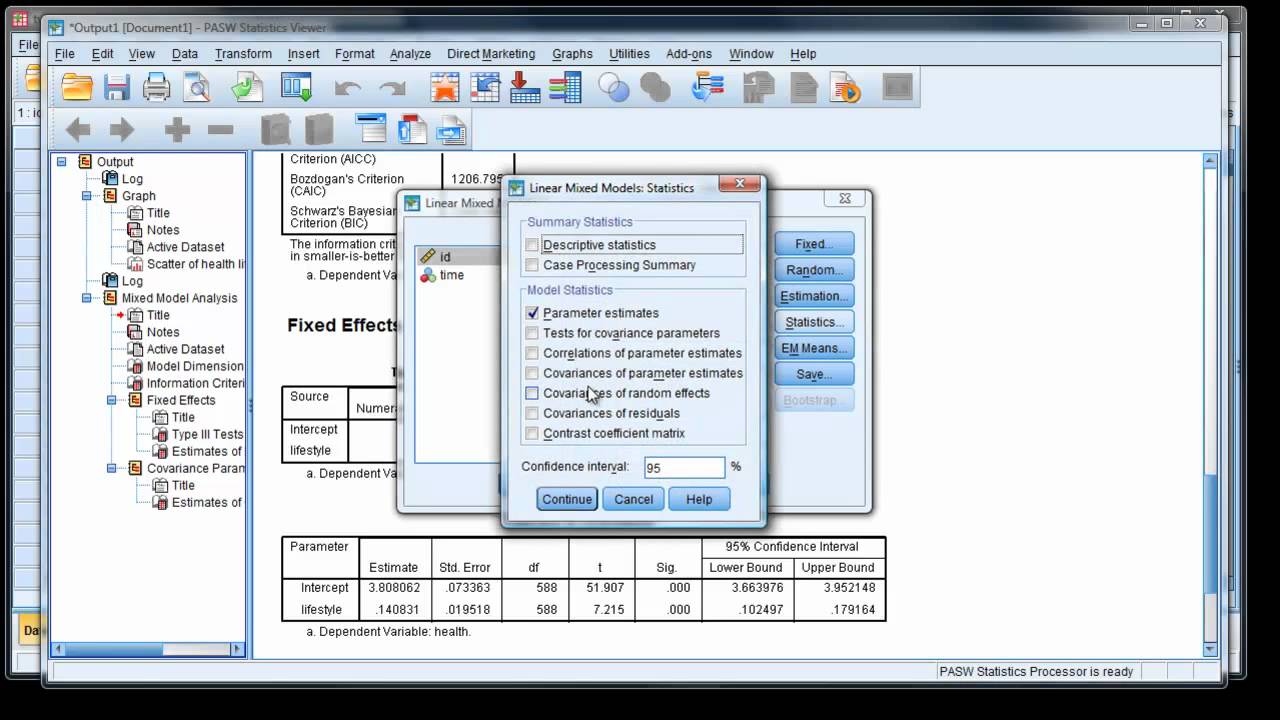
Linear Mixed Models Fixed Effects This feature requires SPSS® Statistics Standard Edition or the Advanced Statistics Option. Fixed Effects. There is no default model, so you must explicitly specify the fixed effects. Alternatively, you can build nested or non-nested terms. Include Intercept. The intercept is usually included in the model.
Comparison of linear mixed effect models without and with temperature
The steps for interpreting the SPSS output for a mixed-effects ANOVA. 1. Look in the Box's Test of Equality of Covariance Matrices table. If the p -value in the Sig. row is MORE THAN .05, continue with the analysis. If the p -value is LESS THAN .05, reassess the observations for outliers and rerun the analysis. 2.

Linear MixedEffects Modeling in SPSS An Introduction to the
The term mixed model refers to the use of both xed and random e ects in the same analysis. As explained in section 14.1, xed e ects have levels that are of primary interest and would be used again if the experiment were repeated.
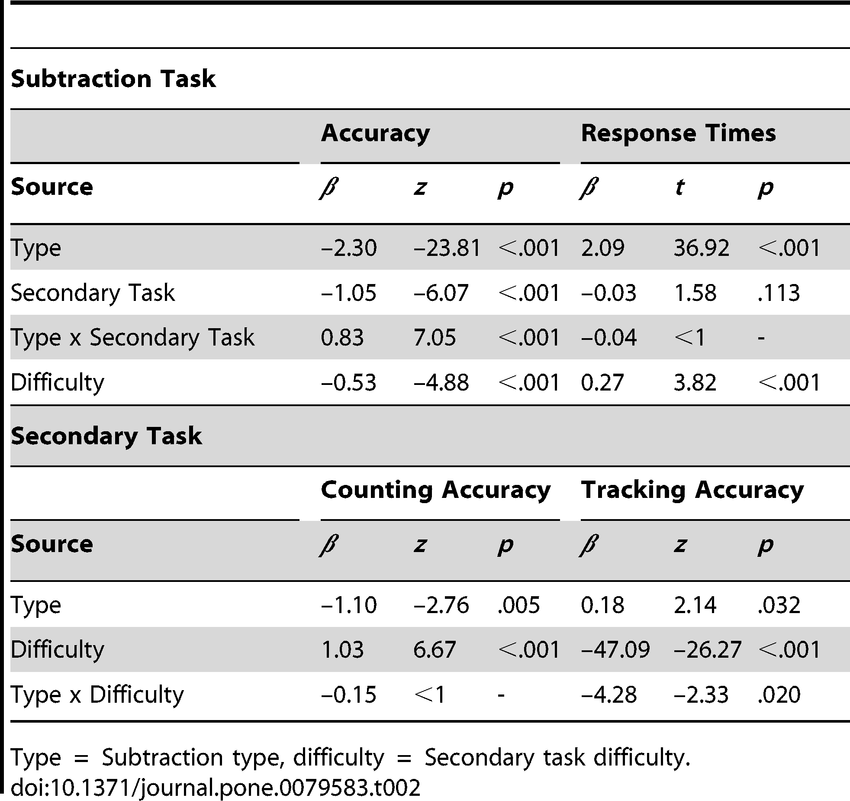
Summary of mixedeffects model results for Experiment 2. Download Table
Linear Mixed Models Random Effects This feature requires SPSS® Statistics Standard Edition or the Advanced Statistics Option. Covariance type. This allows you to specify the covariance structure for the random-effects model. A separate covariance matrix is estimated for each random effect. The available structures are as follows:
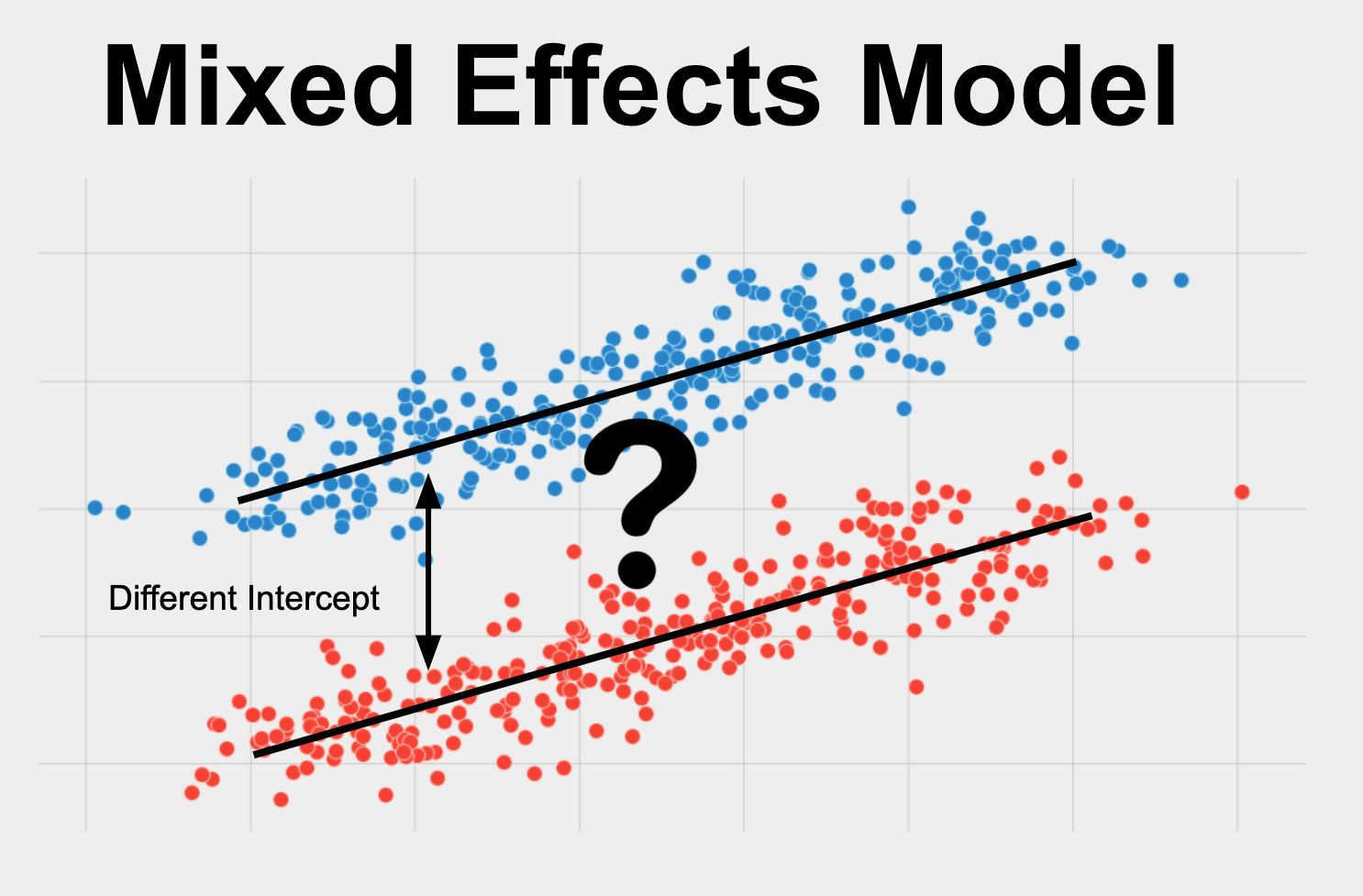
Mixed Effects Model
The Linear Mixed Model; Using Linear Mixed Models to Analyze Product Test Results From Multiple Markets; Using Linear Mixed Models to Analyze Repeated Measurements; Using Linear Mixed Models to Analyze a Crossover Trial; Using Linear Mixed Models to Model Random Effects and Repeated Measures; Using Linear Mixed Models to Fit a Random.

SPSS Advanced Statistics IBM
Although different methods are available for the analyses of longitudinal data, analyses based on generalized linear models (GLM) are criticized as violating the assumption of independence of observations. Alternatively, linear mixed models (LMM) are commonly used to understand changes in human behavior over time.