Dna Diagram No Labels Color worksheets, Dna activities, Dna facts

IB Biology 2 ProProfs Quiz
This experiment demonstrates that DNA-bound hRAD51 locally suppresses intercalator binding, which is in line with our findings in fluorescent intercalator displacement experiments performed in bulk solution on unlabeled hRAD51 bound to DNA ( ).

Dna Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
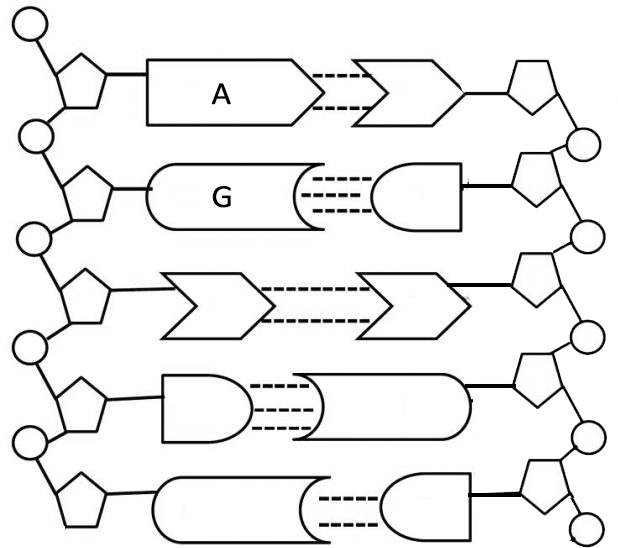
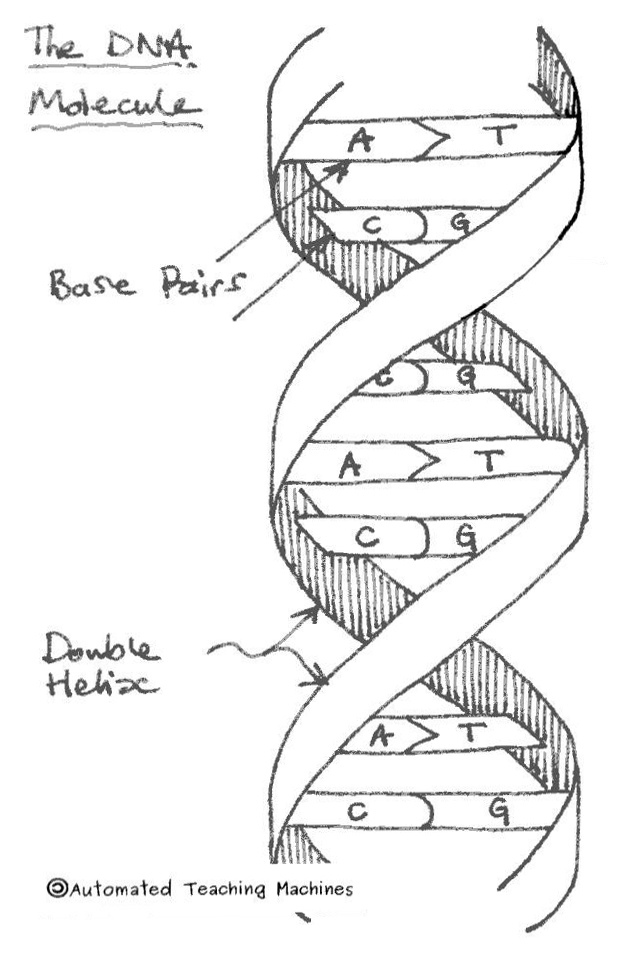
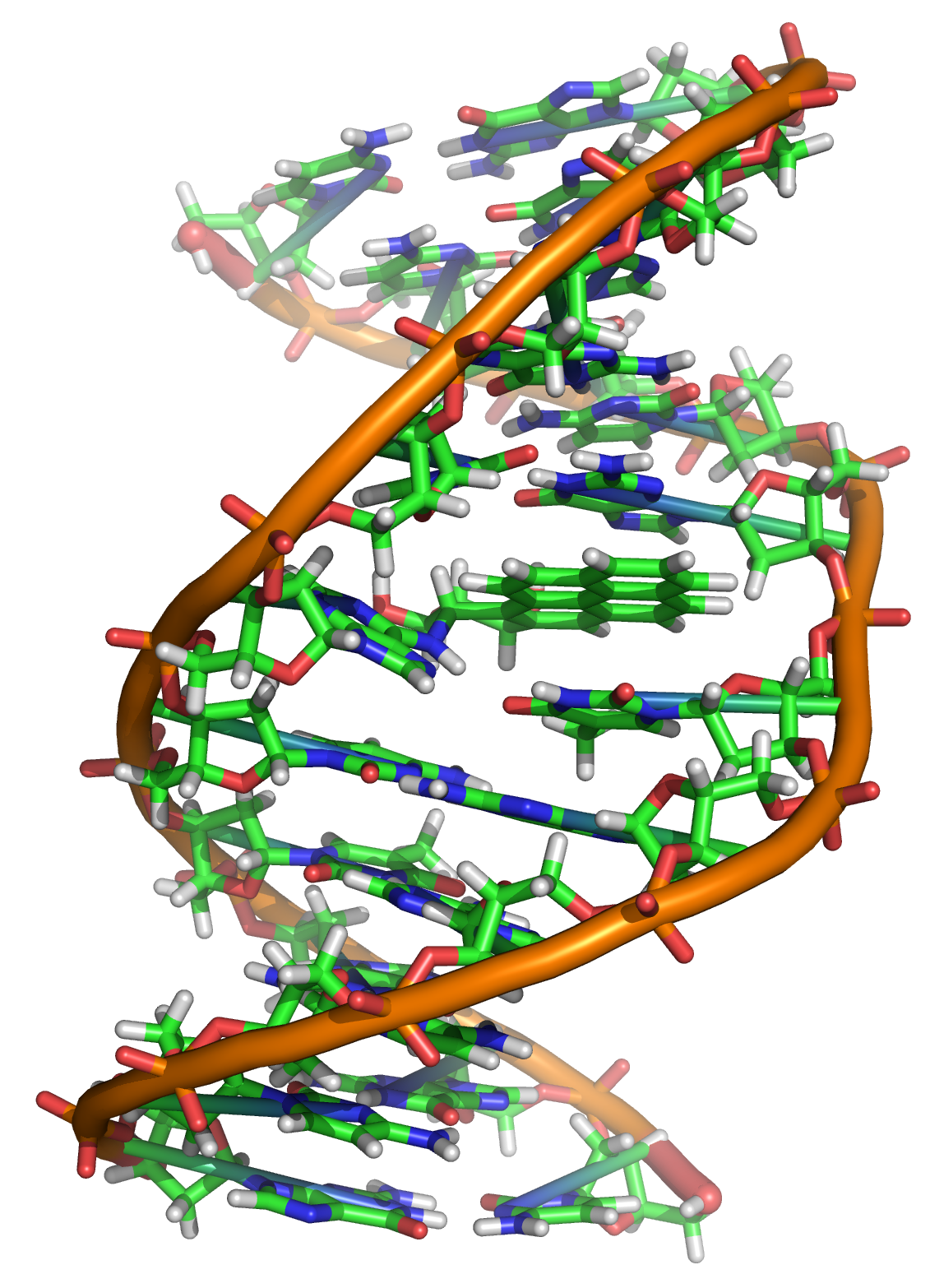
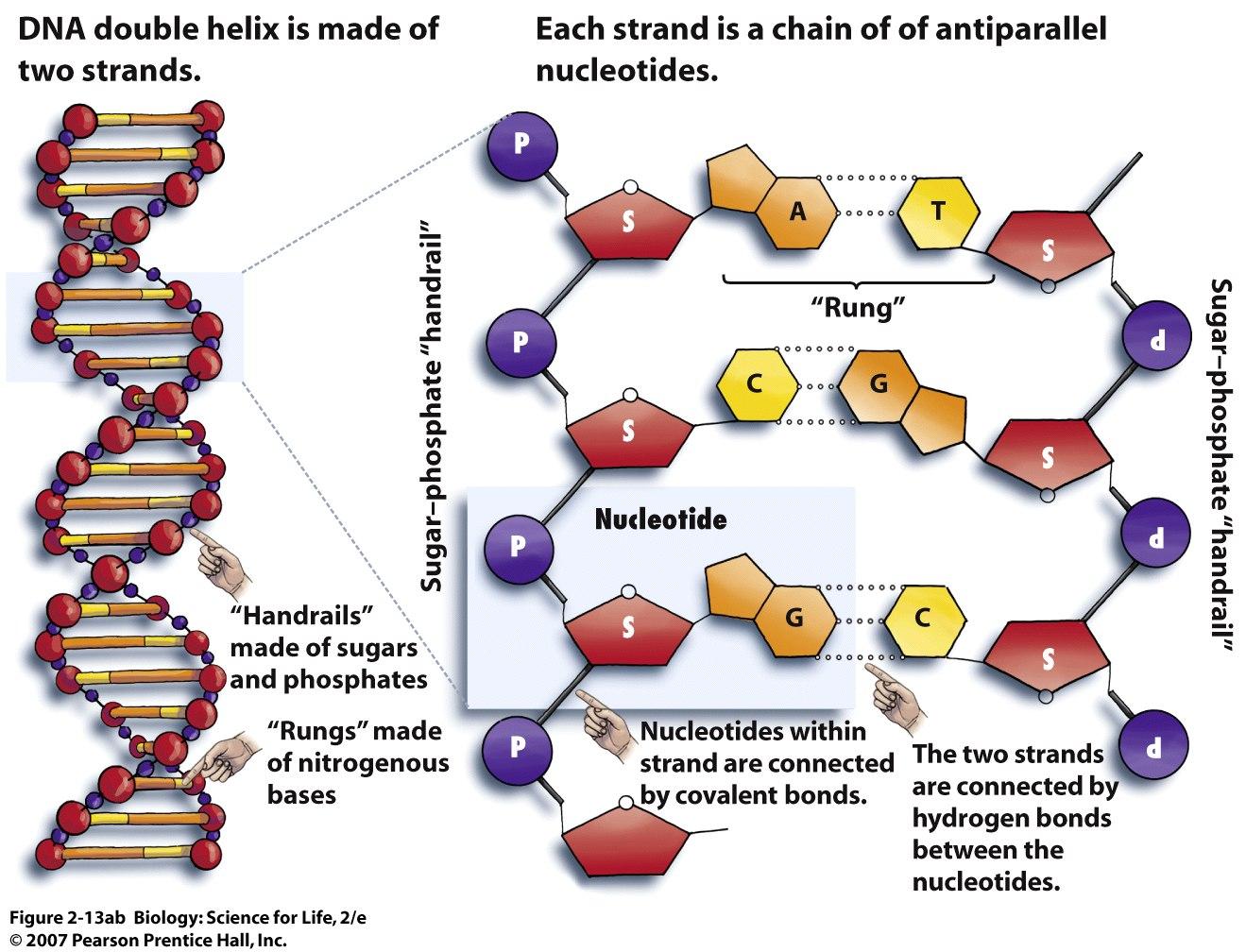
Models of the structure of DNA revealed the molecule is made up of two strands of covalently linked nucleotides that are twisted around each other to form a right-handed helix. In each strand, nucleotides are covalently joined to two other nucleotides (except at the very ends of a linear strand) via phosphodiester bonds that link the sugars via.
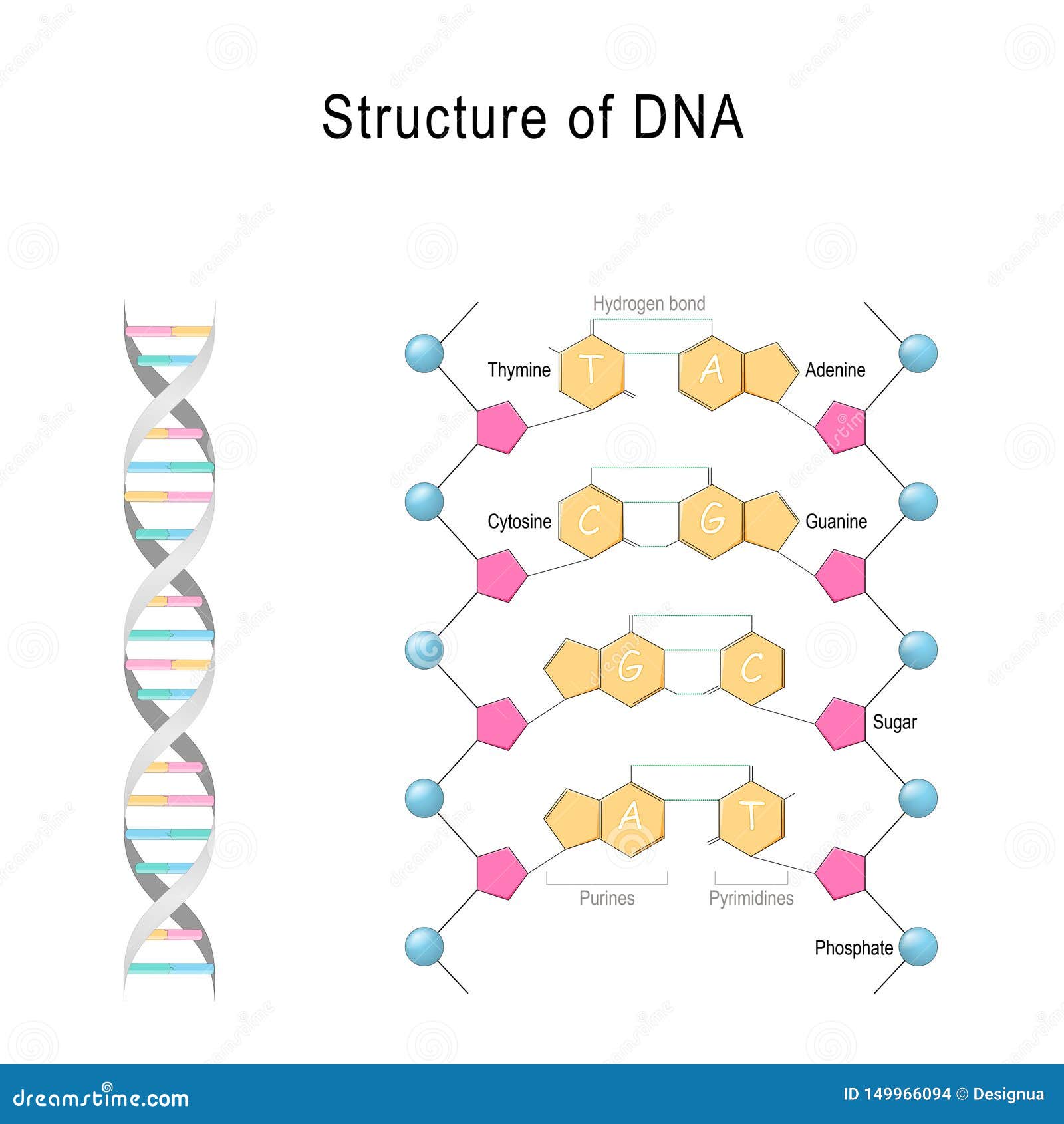
Diagram Of Dna Backbone Dna structure Vector Image 1744634
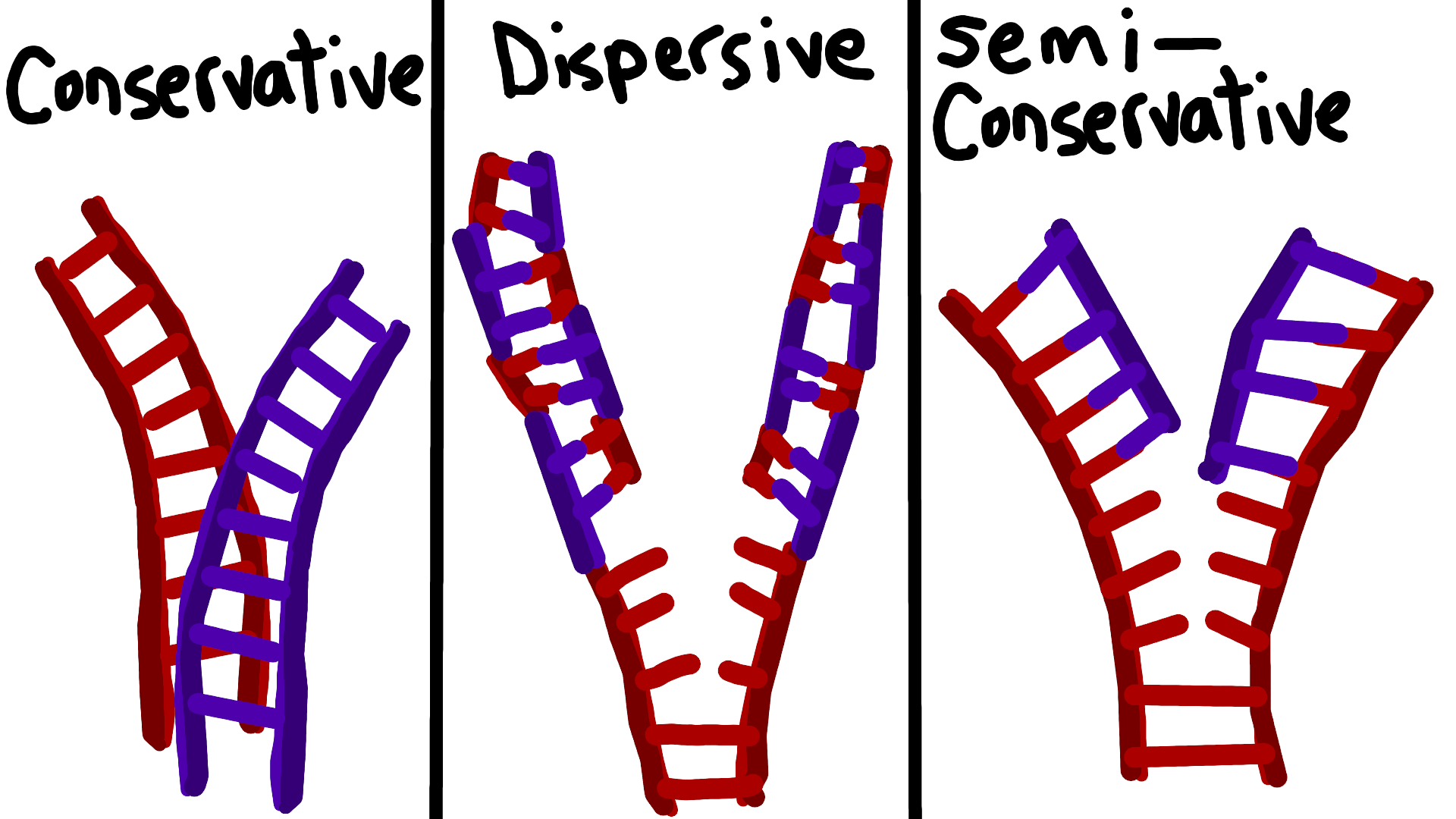
Spoiler alert: The answer is yes! In this article, we'll look at a famous experiment, sometimes called "the most beautiful experiment in biology," that established the basic mechanism of DNA replication as semi-conservative —that is, as producing DNA molecules containing one new and one old strand 3 . The three models for DNA replication

Dna Structure Stock Illustration Download Image Now iStock
15.5: Labeling DNA Probes. DNA probes are fragments of DNA labeled with a reporter tag to enable their detection or purification. The resulting labeled DNA probes can then hybridize to target nucleic acid sequences through complementary base-pairing, and may be used to recover or identify these regions. Radioisotopes, fluorophores, or small.

Given below is a schematic diagram of a portion of DNA. a How many
Nucleotides Structure. Primary Structure of Nucleic Acids: The sequence or order of the nucleotides defines the primary structure of DNA and RNA. The nucleotides of the polymer are linked by phosphodiester bonds connecting through the oxygen on the 5' carbon of one to the oxygen on the 3' carbon of another.

DNA wikidoc
Key points: Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms belonging to the domains Bacteria and Archaea. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells, have no nucleus, and lack organelles. All prokaryotic cells are encased by a cell wall. Many also have a capsule or slime layer made of polysaccharide.

DNA Diagrams 101 Diagrams
DNA replication, or the copying of a cell's DNA, is no simple task! There are about 3 billion base pairs of DNA in your genome, all of which must be accurately copied when any one of your trillions of cells divides 1 . The basic mechanisms of DNA replication are similar across organisms.
Conservation of Material — DNA Replication Expii
Cell diagram unlabeled Learn faster with interactive cell quizzes Sources + Show all What are the parts of a cell? There exist two general classes of cells: Prokaryotic cells: Simple, self-sustaining cells (bacteria and archaea) Eukaryotic cells: Complex, non self-sustaining cells (found in animals, plants, algae and fungi)
Review the Structure of DNA
When they described the double-helical structure of DNA in a one-page article in Nature in 1953, they included this brief statement of a third model:. the addition of 14N, half-labeled and unlabeled DNA are present in equal amounts." A conservative mode of replication is ruled out by the observation that all the DNA formed a band

DNA Online Learning • FamilySearch
Imaging unlabeled proteins on DNA with super-resolution | Nucleic Acids Research | Oxford Academic Journal Article Imaging unlabeled proteins on DNA with super-resolution Anna E C Meijering , Andreas S Biebricher , Gerrit Sitters , Ineke Brouwer , Erwin J G Peterman , Gijs J L Wuite , Iddo Heller
DNA
DNA replication, also known as semi-conservative replication, is the process by which DNA is doubled.This is an important process taking place within the dividing cell. In this article, we shall discuss the structure of DNA, the steps involved in DNA replication (initiation, elongation and termination) and the clinical consequences that can occur when this process goes wrong.
Immunotargeted DNA Nanostructures
The genotype (or genome) is a person's unique combination of genes or genetic makeup. Thus, the genotype is a complete set of instructions on how that person's body synthesizes proteins and thus how that body is supposed to be built and function. The phenotype is the actual structure and function of a person's body.

Base Sequence Of Dna
1 Introduction. End-labeling is a rapid and sensitive method for radioactively, or nonisotopically, labeling DNA fragments and is useful for visualizing small amounts of DNA. End-labeling can also be used to label fragments at one end. All of the enzymes employed are specific to either the 3′ or 5′ termini of DNA and will, consequently.
The Cynical Tendency Making Choices
Recently, Kramer et al. developed DNA probes with a hairpin-shaped structure in which the 5′ and 3′ ends are self-complementary, bringing a fluorophore and a quencher into close proximity.

Painting Acrylic Art & Collectibles DNA
They have short and easy to remember names: A, C, T, G. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nucleobase. (Don't confuse this use of "base" with the other one, which refers to a molecule that raises the pH of a solution; they're two different things.)

Structure Of DNA Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base.