Is Daikon Radish the Same as Horseradish?(Guide) NatureWord

Radish, Daikon Mumm's Sprouting Seeds
Daikon vs Parsnip: At a Glace. In short, Daikon is a white root vegetable that is long and thin and has a moderate flavour. Parsnip, on the other hand, is a beige root vegetable that is sweet and nutty. In contrast to the more prevalent usage of parsnip in European and North American cooking, Daikon is a staple in Asian cooking.

Cow Parsnip vs Giant Hogweed 5 Key Differences Wiki Point
Conclusion. In conclusion, parsnips and daikons are two root vegetables that have unique characteristics and uses in various culinary dishes. While parsnips are sweeter and have a nutty flavor, daikons are milder and have a crisp texture. Both vegetables are nutritious and provide numerous health benefits.
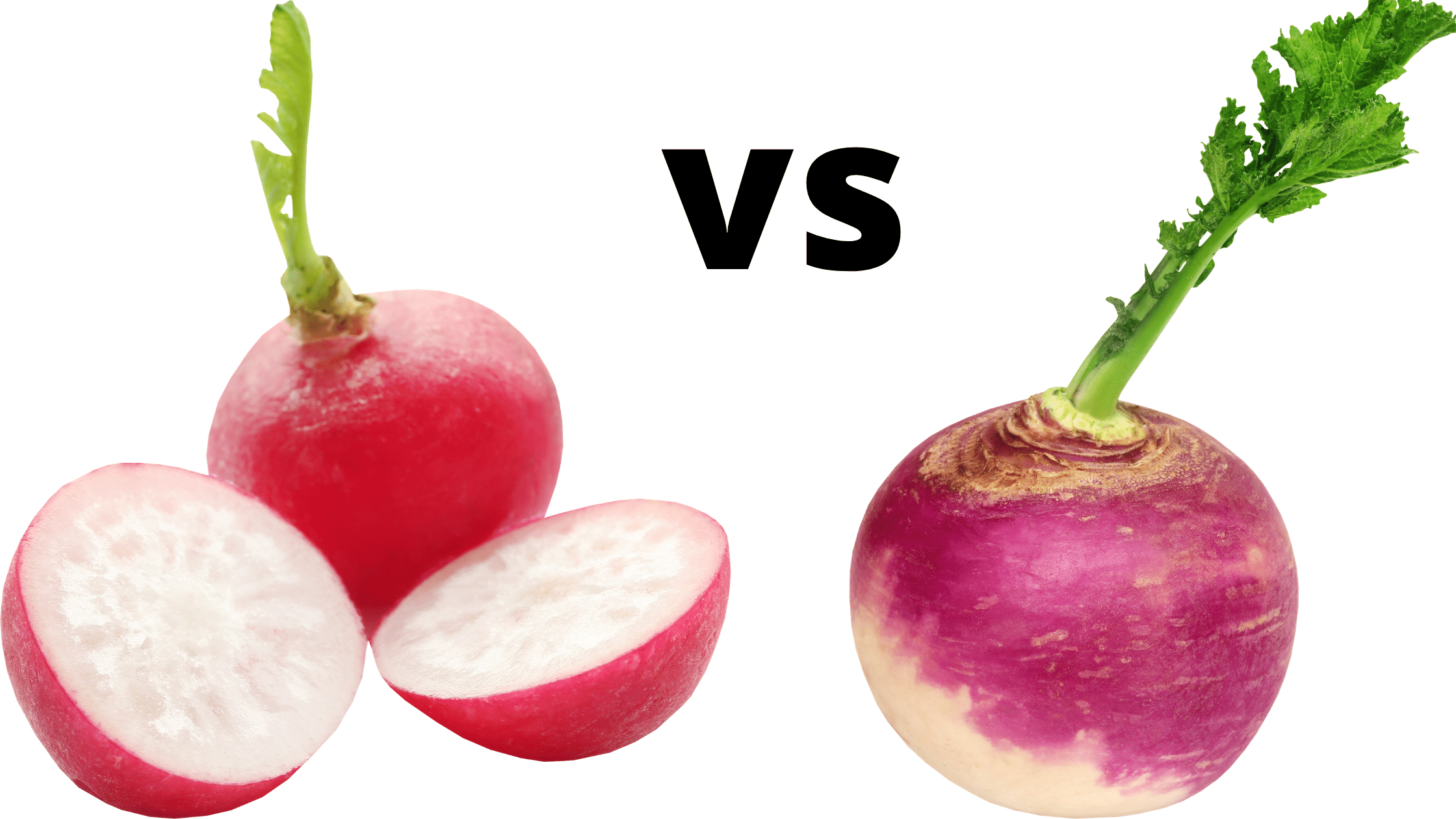
Radish vs Turnip
Parsnip vs Daikon: Which is More Beneficial for Skin Health? Both parsnip and daikon are rich in antioxidants and other nutrients that contribute to healthy skin. Parsnip contains high levels of vitamin C and beta-carotene, which are known to prevent skin damage caused by UV rays. Daikon, on the other hand, is rich in vitamin C, which is.

What's the difference? Wild parsnip vs. golden alexander Forest
Fiber is important for maintaining digestive health and promoting feelings of fullness. A 100-gram serving of turnips contains approximately 1.8 grams of fiber, while a 100-gram serving of radishes contains approximately 1.6 grams of fiber. Turnips are also a good source of antioxidants.

Beet Onion Jicama Turnip Radish Rutabaga Parsnip Carrot Manualzz
Parsnip vs Daikon - Health impact and Nutrition Comparison. Compare Parsnip to Daikon by vitamins and minerals using the only readable nutrition comparison tool.

Root vegetables vector botanical illustration. Carrot, parsnip, daikon
Daikon (also known as Japanese radish and Chinese radish) is a winter radish that's native to East Asia. The word "daikon" comes from the Japanese word for "big root." It's also common in South Asian cuisines (where it's known as mooli) such as Indian, Pakistani, and Bangladeshi. The root veggie, which usually resembles a large white carrot, is.

How are Turnips and Parsnips Different
8% of the RDI. Zinc: 7% of the RDI. Vitamin. B6: 7% of the RDI. In addition to the nutrients listed above, parsnips contain a small amount of calcium, iron, and riboflavin. Summary Parsnips are a.
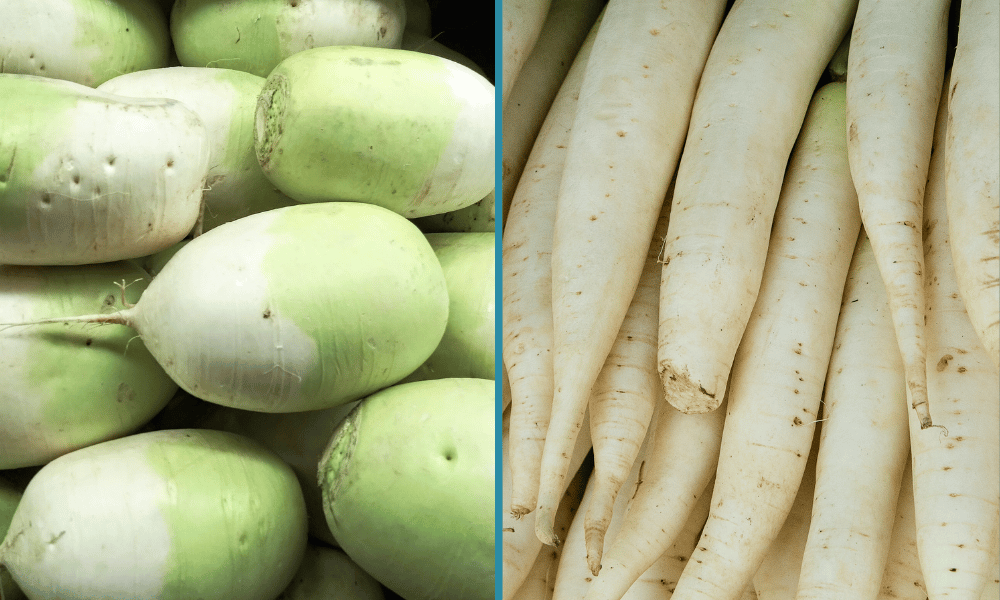
Korean Radish vs Daikon What's the Difference? Let's Foodie
It is a good substitute for daikon radish because of its similar texture and flavor. 4. Parsnips. Parsnips are root vegetables with a cream color and form similar to carrots. You can either use them raw or add them to soups and stews. However, they are tastier when they are roasted, fried, boiled, baked, and steamed.

What Is Daikon? The Crispest, Coolest Vegetable We Know Bon Appétit
A daikon is a winter radish that looks more like a long, white carrot than a red radish, which looks like a small red bulb. Daikon radishes are sweeter, juicier, and less spicy or peppery tasting than their red relatives, among other differences. In the rest of this article, we're going to look at daikon radishes vs red radishes from every.
/Chinese-white-radish-daikon-694717-V2-4b81efa2808c4f40814d15f1b10e5c97.png)
Chinese Red Radish Soup pranploaty
Dietary Fiber Content. Chinese turnip has more dietary fiber than daikon per serving, although both are good sources of fiber. A single daikon contains 5.4 grams of dietary fiber, which provides 14 to 22 percent of the recommended dietary intake of fiber per day. A serving of raw jicama has 16.1 grams of dietary fiber, which provides 42 to 64.

Parsnip SideChef
2 small parsnips, peeled and sliced diagonally in 1/3″ slices or cut in 3/4″ pieces; part of a white or purple daikon radish, peeled and cut into 3/4″ pieces; yellow or red onion, sliced in wedges; 4 - 4 1/2 tablespoons avocado oil; 2 tablespoons fresh oregano, chopped fine; salt; Instructions

Is Daikon Radish the Same as Horseradish?(Guide) NatureWord
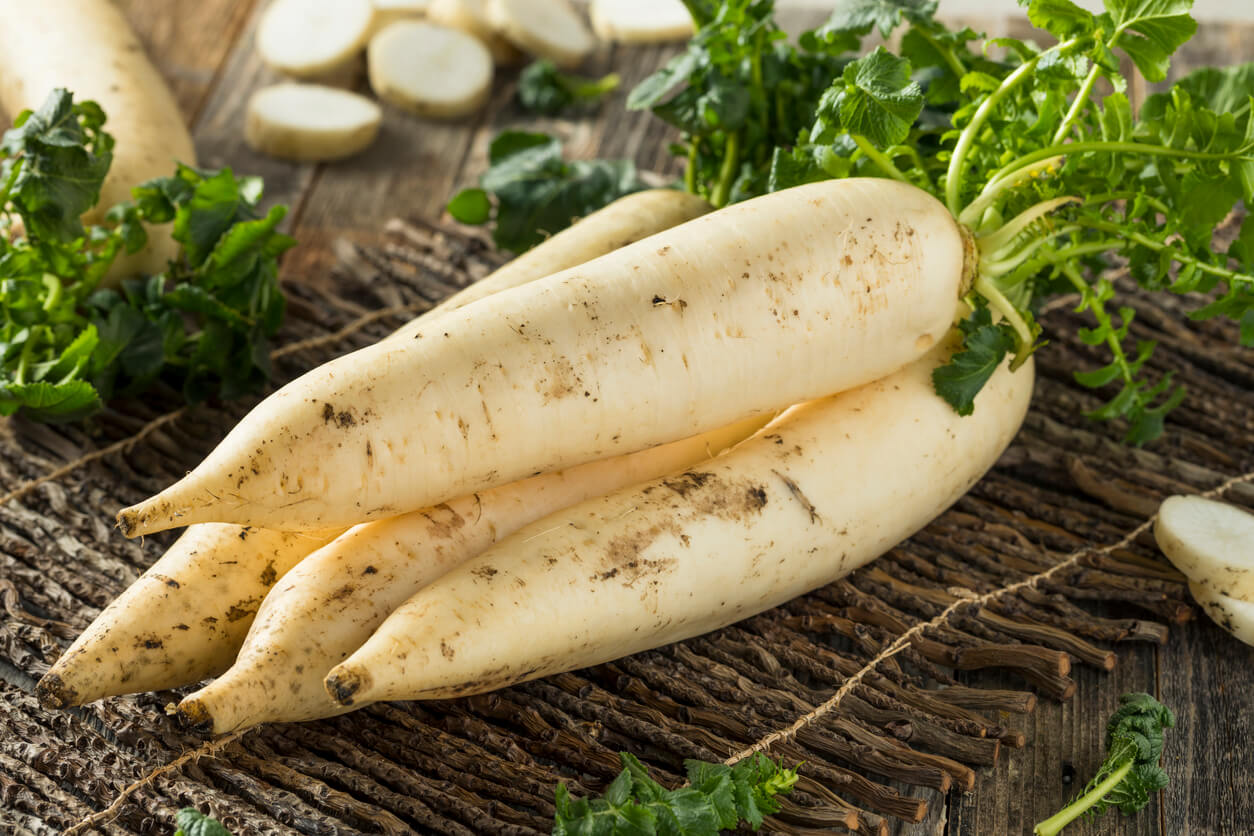
Daikon [2] or mooli, [3] Raphanus sativus var. longipinnatus, is a mild-flavored winter radish usually characterized by fast-growing leaves and a long, white, napiform root. Originally native to continental East Asia, [4] daikon is harvested and consumed throughout the region, as well as in South Asia, and is available internationally.

Daikon Or Japanese Radish Properties, Uses And Benefits Bullfrag
Daikon has more carbs than radishes. The vitamin levels in these veggies are similar, but daikon has a higher percentage of vitamin C and folate, whereas radishes are high in vitamin K and B6. Comparatively, daikon is high in minerals like phosphorus and magnesium, but both vegetables are similar in calcium and potassium.

Daikon Description, Plant, Root, Definition, & Facts Britannica
In the case of Korean radish and daikon, their differences are more underhanded and less obvious: Soft Or Firm - When raw, Korean radish and daikon are just as crunchy as one another. However, only Korean radish is able to retain that crunchiness once cooked. Daikon tends to soften up quickly so will only remain crunchy if cooked for a few.

What Is The Difference Between Daikon And Radish Reviewho
As nouns the difference between parsnip and daikon. is that parsnip is a biennial plant, species: Pastinaca sativa, related to the carrot while daikon is an East Asian cultivar or subspecies of radish ( Raphanus sativus) bearing a large, white, carrot-shaped taproot consumed throughout East and South Asia but grown in North America primarily as.

Daikon (daikonnyaki) / Twitter
Micronutrients. Daikon consists of about 95% water, whereas parsnip consists of about 80% water. The content of micronutrients in parsnips is higher than that of daikon. Parsnips have more protein, carbs, fiber, and monounsaturated fats than daikons. These vegetables lack trans fat.