Cross Section Of Corn Stock Photo Image 40342087

Corn Stem (CrossSection) Prepared Microscope Slide
When corn seed is horizontally filled into the hole, there may be six filling poses of seeds in the cross-section direction of the hole seed-metering wheel, as shown in Figure 3. When the corn seed is turned 90° to fill the hole, there may be three filling poses in the cross-section direction, as shown in Figure 4.

Corn Branch Root Zea mays root cross section with lateral … Flickr
Filo gèn. CC BY-SA 4.0 ). Learning objectives By the end of this lesson you will be able to: List three functions of a seed and name the seed part that has that function. Identify the parts of the embryo and the structures they become. List the types of nutrients that are stored in seeds.
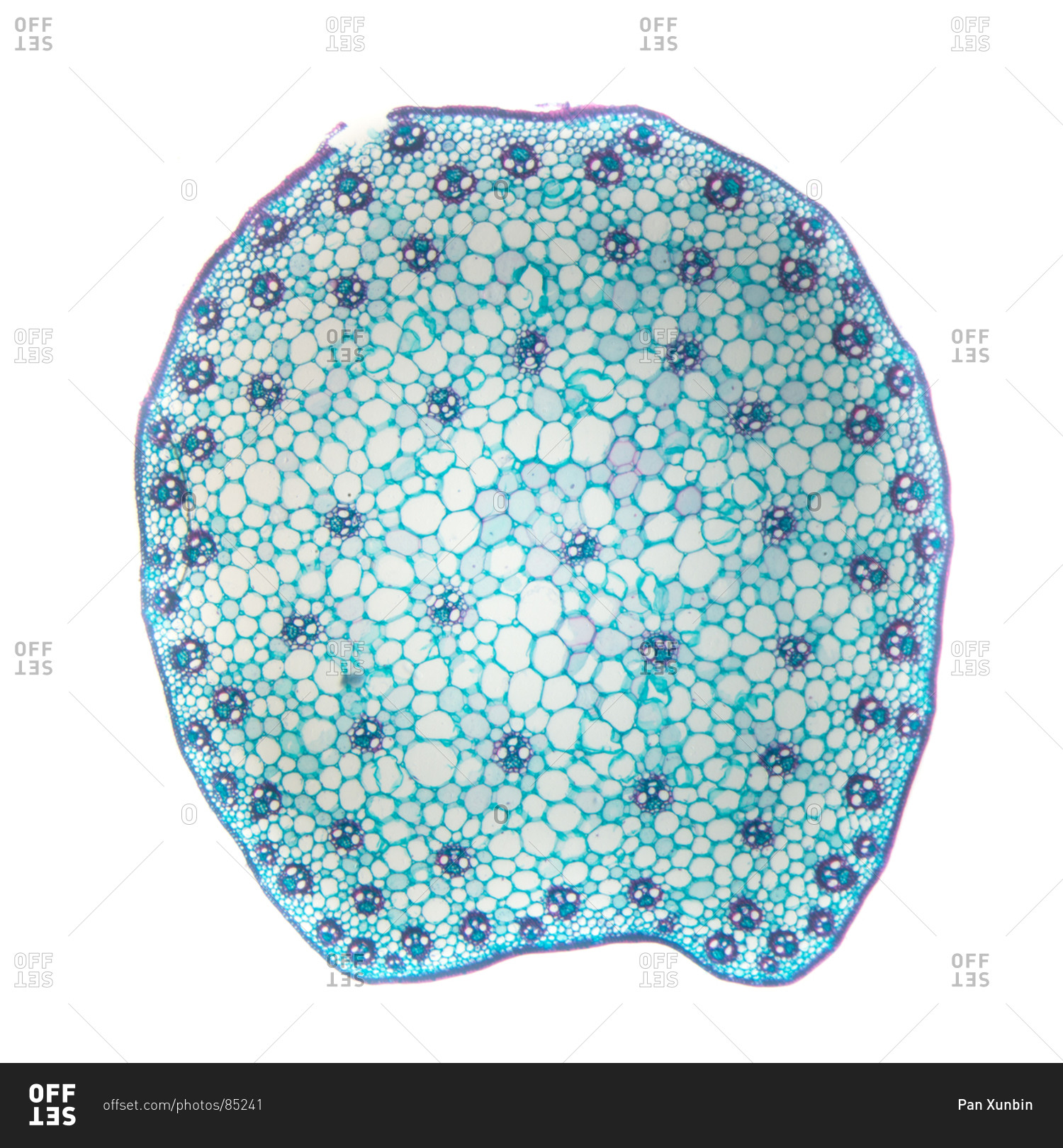
Corn stem cross section, with typical monocot arrangement of vascular bundles stock photo OFFSET
The ground tissue is separated into an outer cortex and a central pith. The epidermis borders the entire stem. Image labeled from Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library (public domain) Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\): Cross section of a corn (Zea mays) stem, an example of an atactostele, at 40X magnification. Vascular bundles are.
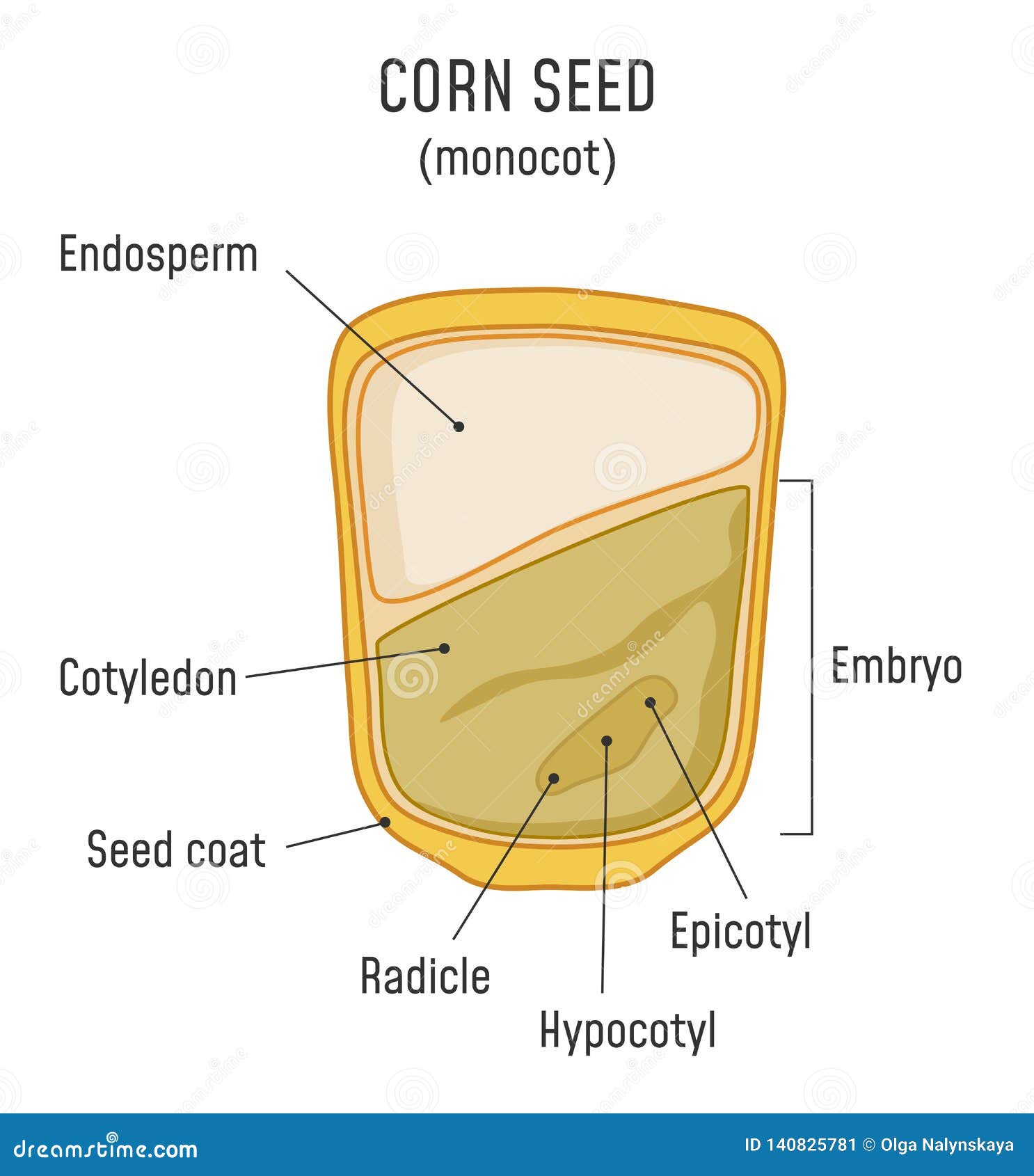
Corn Seed Structure Monocot Stock Vector Illustration of grain, bean 140825781
Browse 70+ corn seed vegetable cross section stock photos and images available, or start a new search to explore more stock photos and images. Sort by: Most popular. Corn on the cob kernels peeled isolated on white background Fresh yellow corn on white background corn seed vegetable cross section stock pictures, royalty-free photos & images.

Longitudinal crosssection of corn kernel [98]. Download Scientific Diagram
12-frame longitudinal cross-section of a corn seed. November 5, 2011 Greg Leave a comment. A x20 magnification micromosaic using 12-frames of a longitudinal cross-section corn seed taken using the Canon 5D MkII and the research trinocular microscope.
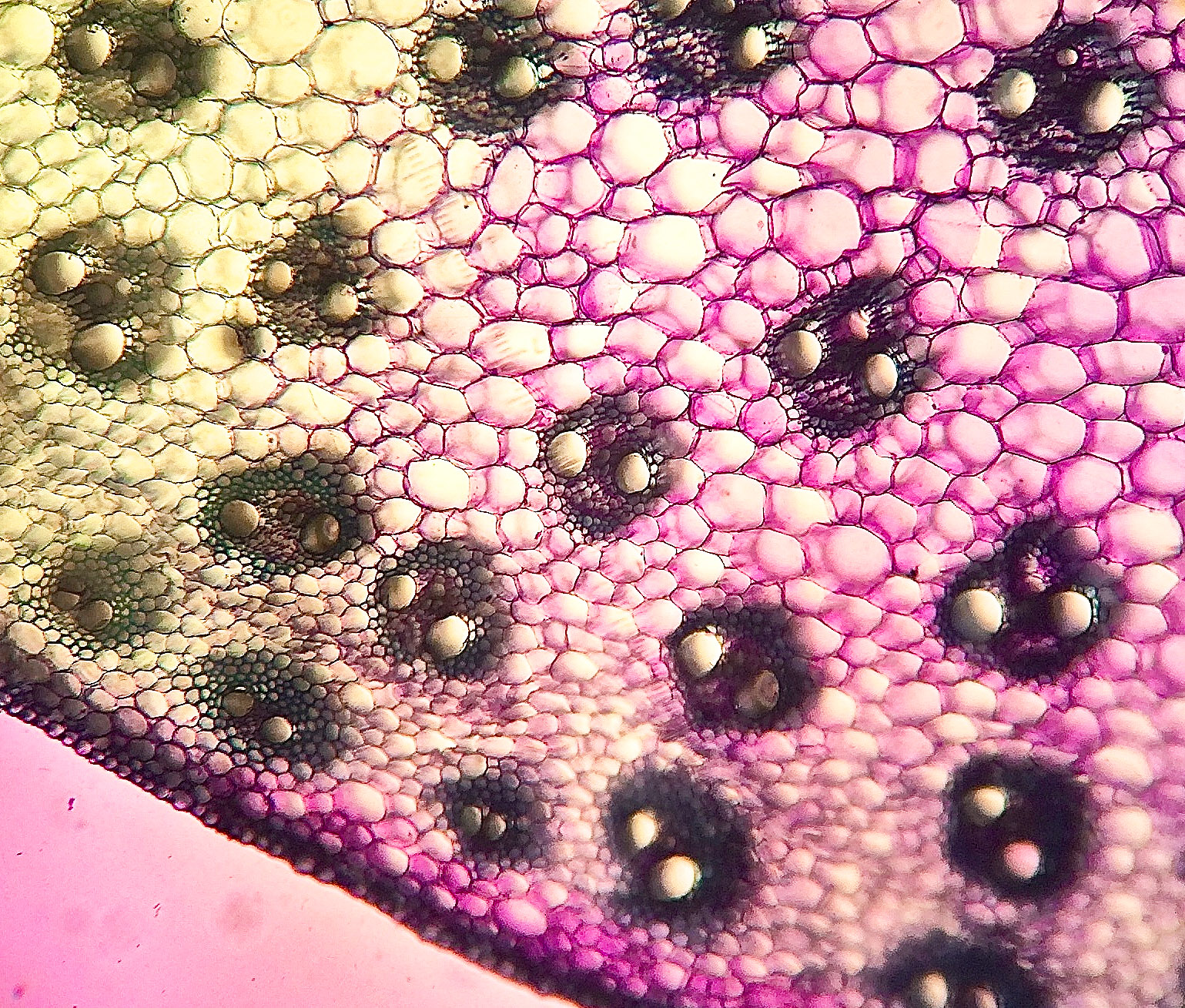

Jan Xue’s corn stem crosssection BIOL/APBI 210 Lab Information
Cross sections of kernels from corn varieties classified as hard (A), intermediate (B), and soft (C), showing maximum ranges of vitreous and floury endosperm within each variety (I mostly floury and III, mostly vitreous).. 100% female, will eventually form the pericarp that in the specific case of cereals is firmly attached to the seed. In.

Anatomy Of A Corn Kernel Anatomical Charts & Posters
Figure 4.6.3.1 4.6.3. 1: The external structures of a bean seed, an example of a eudicot (7X). The seed coat surrounds the seed. There is a round micropyle, where the pollen tube originally entered the ovule. The oval hilum is a scar from where the ovule was attached to the ovary. Image by Melissa Ha ( CC-BY ).

Corn cross section isolated on white background Stock Photo Alamy
License: CC BY: Attribution. 5.1: Seed Plants Lab is shared under a CC BY 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. In this lab, you will observe samples of seed plants as well as their structures and determine the characteristics of each plant while explaining the functions of each part. After, you will be able..

2. The corn kernel structure. Download Scientific Diagram
Grades K-2: Parts of a Corn Seedling » » The Parts of a Corn Seedling (Zea mays, Monocotyledon) Part of the Biodiversity Counts Curriculum Collection. More in Plant Morphology Monocotyledon: Monocotyledon embryos have one cotyledon that absorbs food. Monocots usually have narrow leaves with parallel veins, and flower parts in multiples of three.

Corn cob cross section. stock image. Image of isolated 21038899
1. Seed and Seedling Soaked and dry seeds of a monocot (corn) and a dicot (bean) are provided. A. Monocot - These seeds have only one cotyledon (seed leaf). Place the flat side of the corn kernel on several paper towels. With a sharp Show transcribed image text There are 2 steps to solve this one. Expert-verified Step 1 View the full answer Step 2

Corn cross section hires stock photography and images Alamy
The Seed: The Beginnings Of The Corn Plant Look at a corn cob - you will see the seeds! The kernels that you eat can also be used as the seed source to start new plants. Don't worry; the corn kernels that you eat won't grow in your stomach. Specific corn plants are set aside to provide seed. Corn Growth Stages
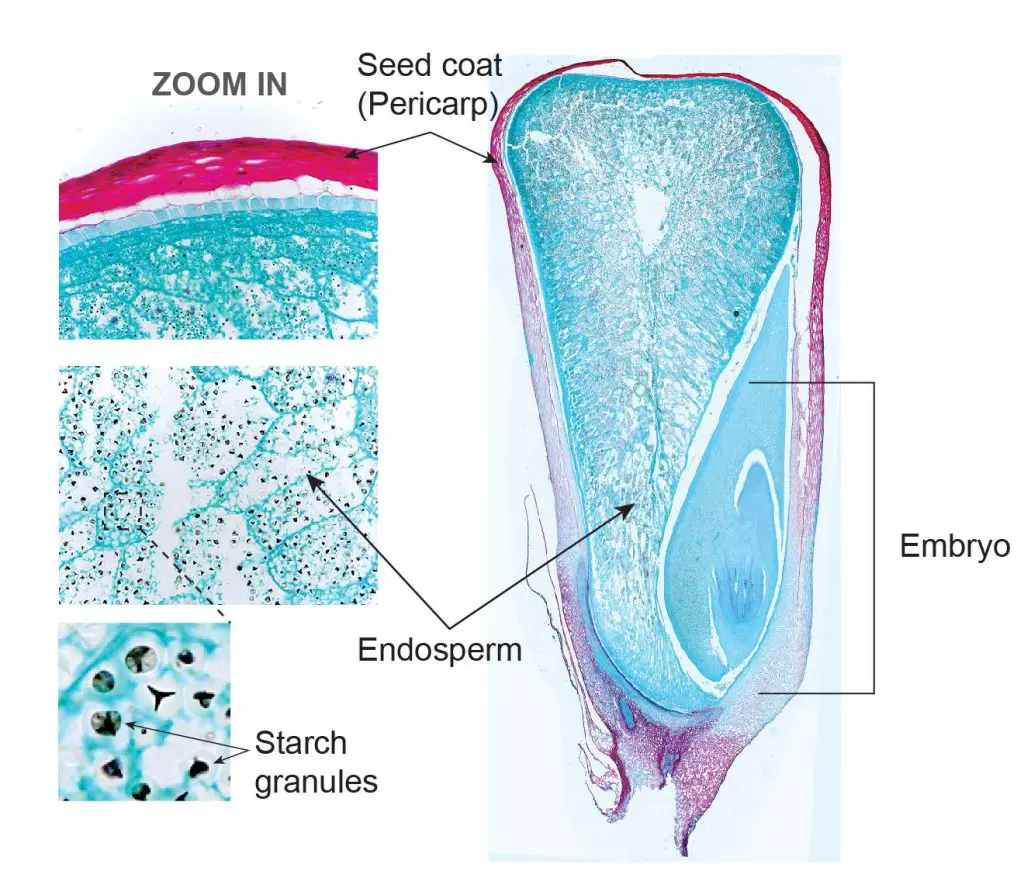
Plant tissue under a microscope xylem and phloem Rs' Science
Zea mays. Zea mays (corn) is often used as a model organism for monocot anatomy. Figure 11.1.2.1 11.1.2. 1: The images above show a corn seedling in two different stages of development. The first image is of the corn seedling at an earlier stage. It has produced a shoot (with one cotyledon) and a long root (radicle).

Cross Section Of Corn Stock Photo Image 40342087
In a cross section of the embryo, the rudimentary parts of the ultimate corn plant are evident—for instance, the plumule with stem and leaves and the primary root.. Corn seed sales in the United States are very competitive, especially with the large number of buyouts and mergers that have occurred since about 1997. As a result of.

Monocot Germination Corn Seedling photo Plant science, Botany, Biology plants
The corn kernels are seeds that develop on the ear after fertilization. Also shown is the lower stem and root. If both male and female flowers are borne on the same plant, the species is called monoecious (meaning "one home"): examples are corn and pea.. Shown is (a) a cross section of an anther at two developmental stages. The immature.

Corn Seed Diagram images
S uccessful emergence (fast & uniform), while important, does not guarantee successful stand establishment in corn. The next crucial phase in the life of young corn plants is the initial establishment of a vigorous nodal root system. Successful stand establishmend is largely dependent on the initial development of nodal roots from roughly V2 (two leaves with visible leaf collars) to V6.
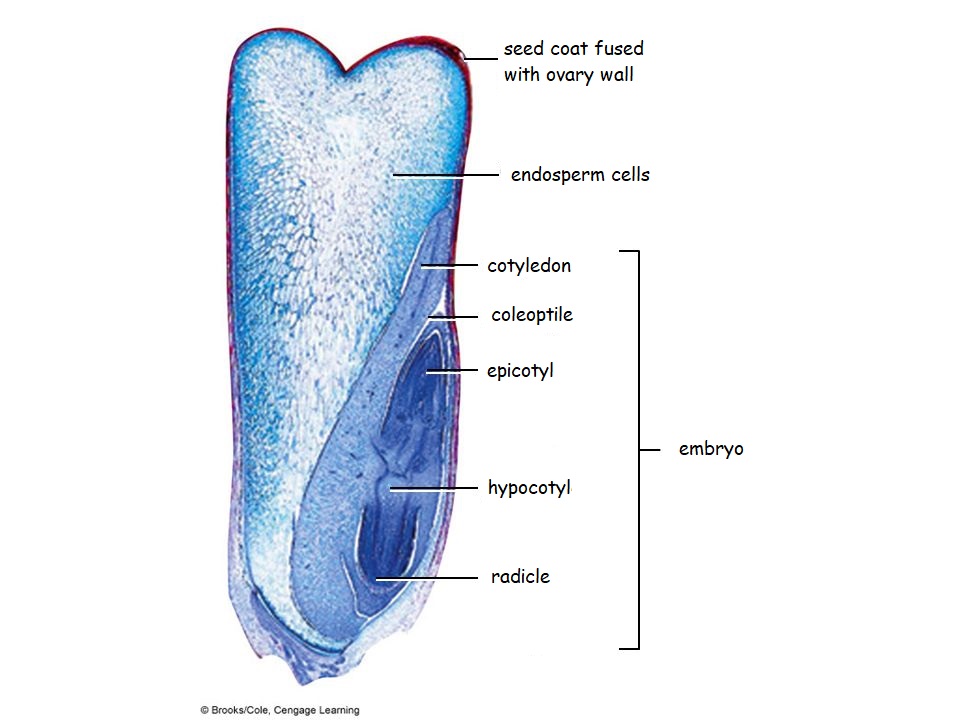
Biology 2
Describe the general characteristics seed plants. Name the phyla discussed in the lab and give an example of a plant from each. Recognize and identify plant specimens viewed in the lab, both slides and live samples. Understand the basic gymnosperm and angiosperm life cycle. Recognize the difference between a male and female pine cone.