4 Important Properties Of Enzymes Infinita Biotech

Enzymes HARVEST SPOON
In conclusion, using a metal spoon to scoop raw honey may not necessarily kill enzymes in honey. However, it is important to note that honey is acidic due to its organic acid content, and the pH scale of honey is normally between 3.4 to 6.1. Acidic substances can corrode metals, and it is often feared that metal components can be mixed in honey.
4 Important Properties Of Enzymes Infinita Biotech
Some experts believe that honey when honey comes in contact with metals like copper or iron (commonly found in spoons) these metals are capable of destorying beneficial enzymes. Metals like copper and iron react with the acids in honey to produce salts. This process kills off useful enzymes. Copper is known to react with acids in honey.

Horizontal rustic with spoon affect buttercream design. Buttercream
Honey is known for its content of biomolecules, such as enzymes. The enzymes of honey originate from bees, plant nectars, secretions or excretions of plant-sucking insects, or from microorganisms such as yeasts. Honey can be characterized by enzyme-catalyzed and non-enzymatic reactions. Notable examples of enzyme-catalyzed reactions are the.
bolita Último Pisoteando anatomia apis mellifera suéter puente Condensar
However, we do not recommend storing a metal spoon within your honey for long periods of time. 7. Honey can be used on wounds Fact. Up until the early 20 th century, honey was used as a conventional therapy in fighting infection. 8. All bees produce honey Myth. There are nearly 20,000 known bee species in the world. From this number, only 5%.

Honey Lemon Enzyme Recipe
Myth 4: Do not scoop honey with a metal spoon. It is a known fact that honey is a bit acid, and same as any edible acid; if it stays on metal for long, it can destroy the metal. However, scooping honey with a metal spoon is such a quick process that it cannot damage it. At the same time, we do not recommend leaving a metal spoon in the honey.
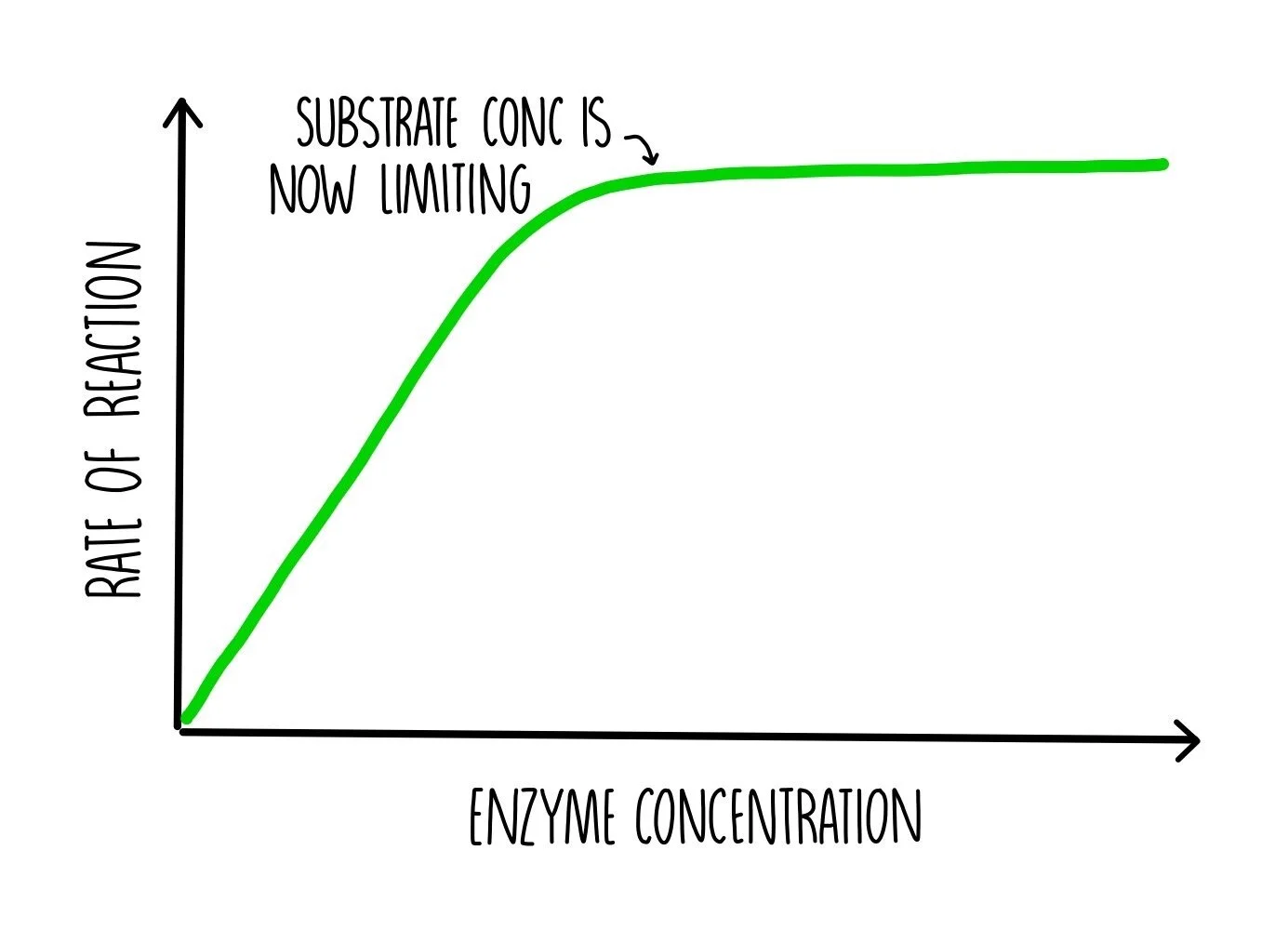
Enzymes (ALevel) — the science sauce
Honey is known for its content of biomolecules, such as enzymes. The enzymes of honey originate from bees, plant nectars, secretions or excretions of plant-sucking insects, or from microorganisms such as yeasts. Honey can be characterized by enzyme-catalyzed and non-enzymatic reactions. Notable examples of enzyme-catalyzed reactions are the production of hydrogen peroxide through glucose.

Honey In Spoon Stock Photo Image 4917040
Honey is known for its content of biomolecules, such as enzymes. The enzymes of honey originate from bees, plant nectars, secretions or excretions of plant-sucking insects, or microorganisms such as yeasts. Honey can be characterized by enzyme-catalyzed and non-enzymatic reactions. Notable examples of enzyme-catalyzed reactions are the production of hydrogen peroxide through glucose oxidase.

Raw Honey Enzymes Raw honey, Enzymes, Honey
The theory behind this claim is that the ions present in metal can react with the enzymes in honey, causing them to break down and lose their functionality. However, scientific research on this topic has yielded mixed results, with some studies suggesting that metal spoons can indeed affect honey enzymes, while others have found no significant.

Did you know that... there are living enzymes in honey? Did you know
All Bees Do Not Produce Honey. One of the most common misconceptions about raw honey is that it can come from any type of bee. It is estimated that out of 20,000 known species of bees in the world, only 5% are able to produce edible honey. The only kind of bee that can make it is the honeybee. The honeybee species is one that lives in large.
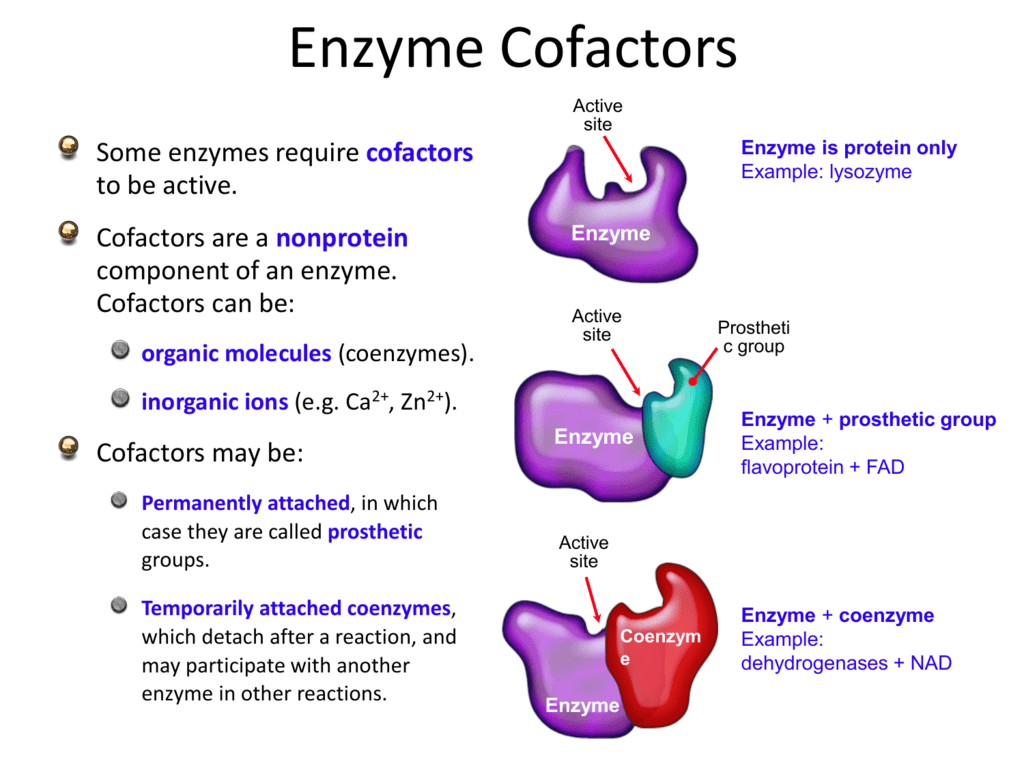
Enzyme Cofactors
With regard the proteolytic enzymes of honey, it is known that honeybees use three midgut endopeptidases (trypsin,. E-64, specific for cysteine proteases; and 1,10 phenantroline, specific for metallo-proteinases, had no effect at the concentration used. All the inhibitors mentioned above, as well as Pepstatin A, were ineffective in gelatin.

Question Video Describing How Enzymes Affect Biochemical Reactions
Even though honey is acidic, it only takes a few seconds to scoop out honey with a metal spoon so the spoon will not get corroded at all.. It can also destroy some of the natural enzymes in honey that are healthy for you. 4. Honey's quality is not affected by crystallization. This is another important fact about honey. Crystallization.

Types Of Honey From Flowers Do Different Flowers Make Different Honey
The pH scale of honey is normally between 3.4 to 6.1 and acidic substances can corrode metals and it is often feared that metal components can be mixed in honey, such as metal spoons or other metal utensils. So is it bad to use metal spoon with honey? In respect to this, not all honey has the same level of acidity.
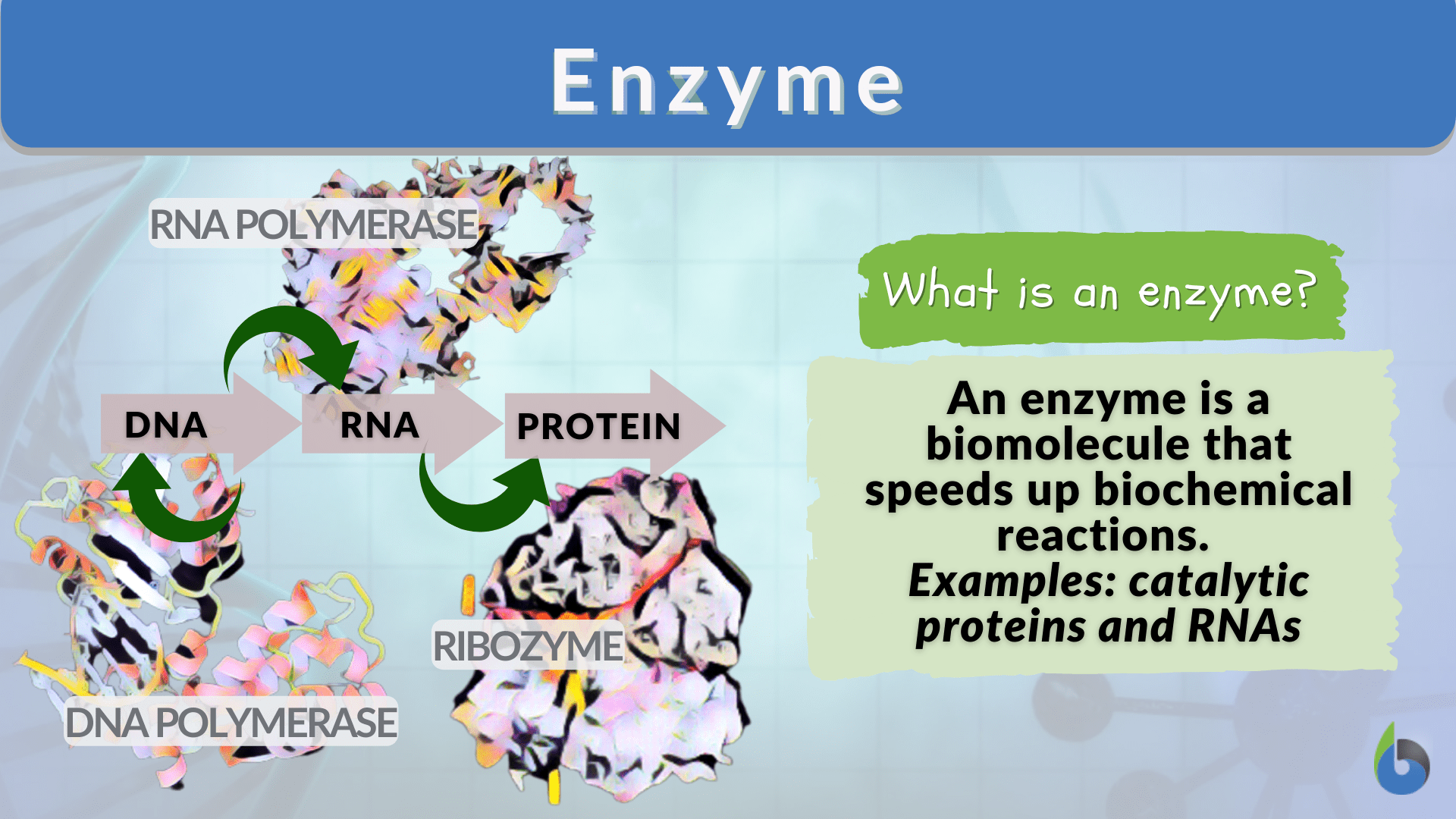
Enzyme Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
The other enzymes in honey are affected similarly. Enzyme activity stops when honey is held at freezing temperatures but returns when warmed back up. It does not return when destroyed by heat. Two interesting side notes are that almost all the enzymes in honey are introduced by the bees, and all break down when liquefying crystallized honey in.
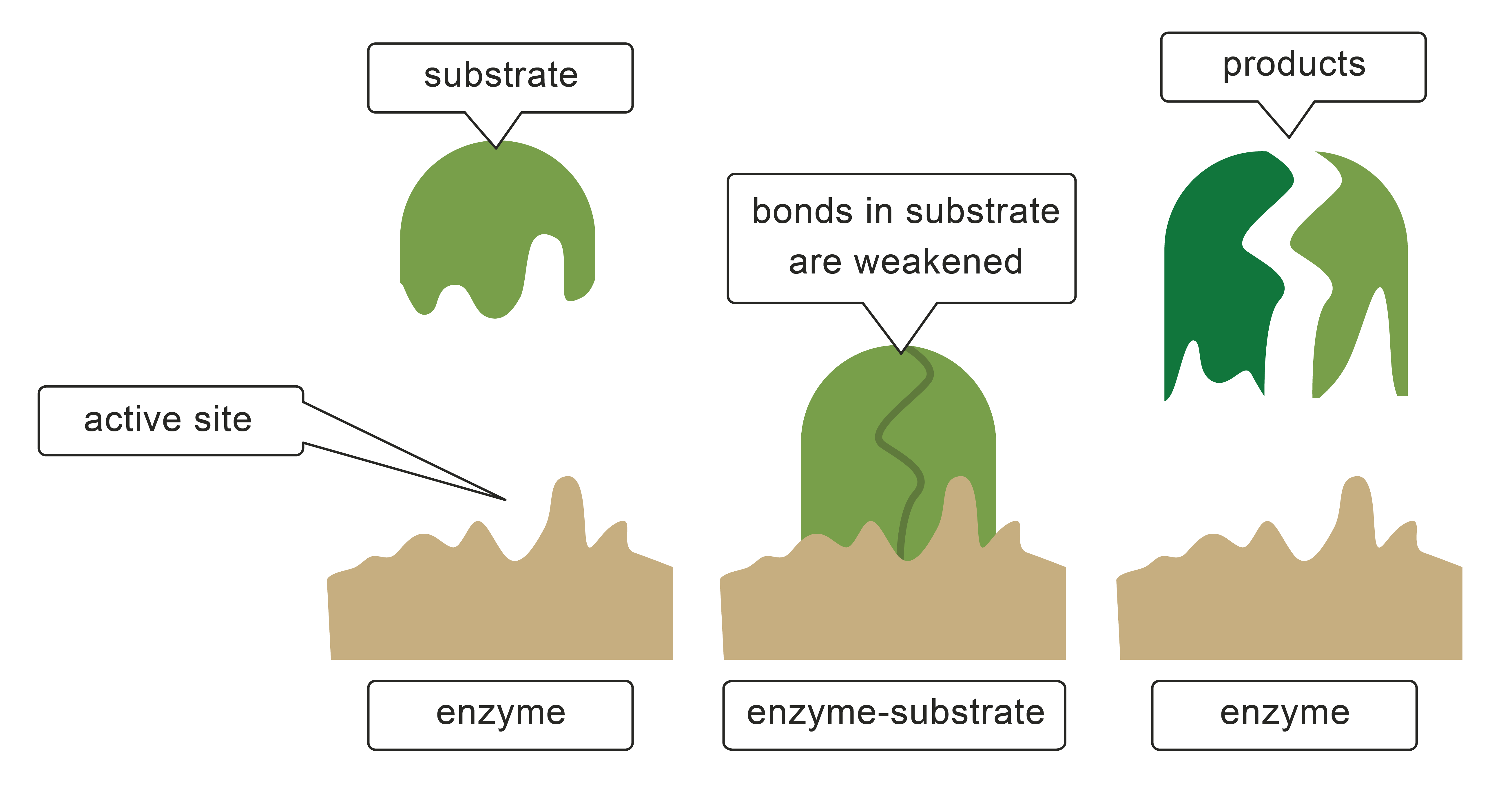
Enzymes I The Unsung Heroes of the Body The Essential Way
Honey enzymes originate from three major sources: plant nectars and secretions, honeybees, and excretions of plant-sucking insects. Biochemical reactions can be divided to two types: enzyme-catalyzed and non-enzymatic reactions [ 4 ]. Enzyme-catalyzed reactions in honey are known to affect its quality and biological activities [ 5, 6, 7 ].
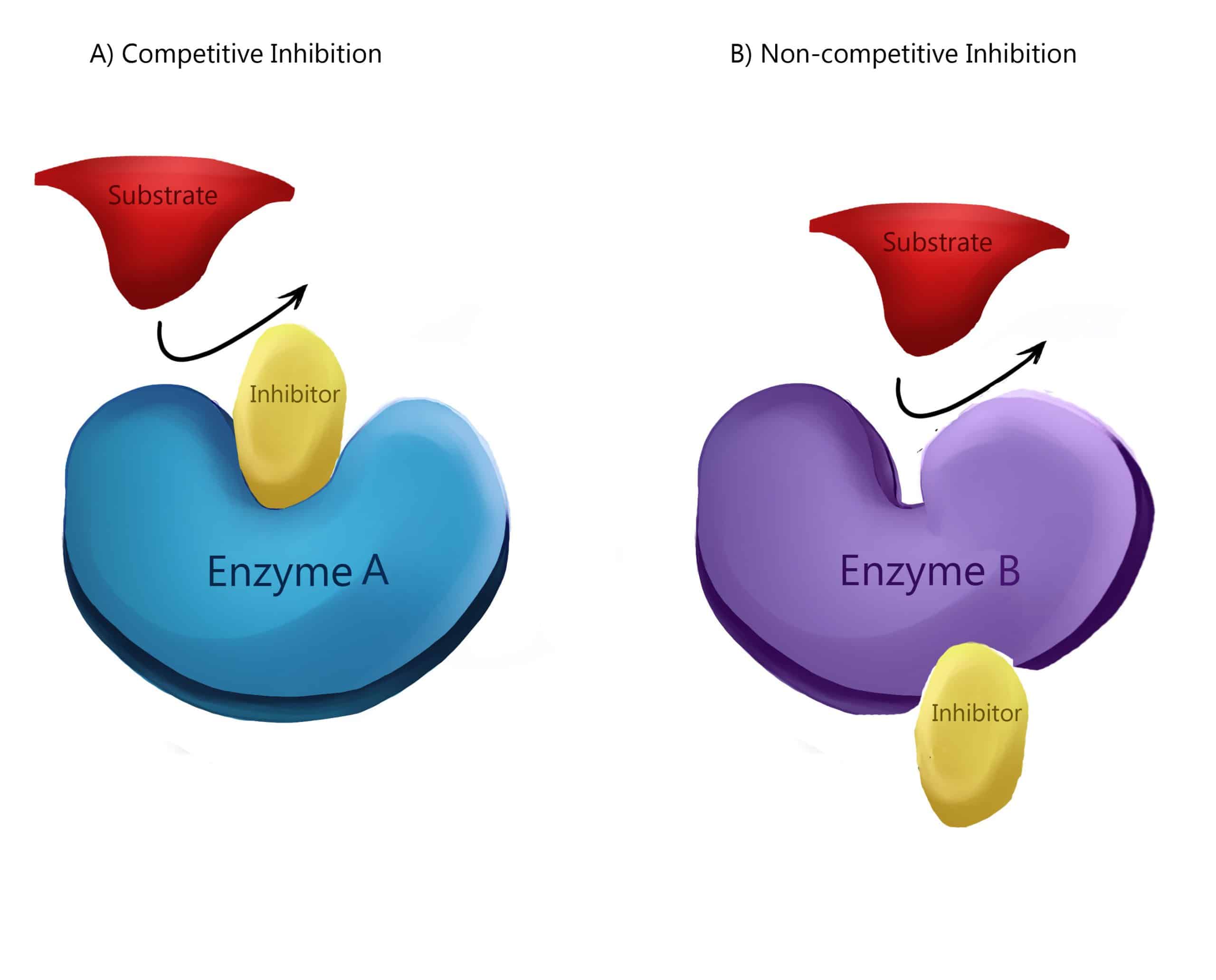
Enzyme Inhibition Types of Inhibition TeachMePhysiology
Honey is acidic due to its organic acid content. The pH scale of honey is usually between 3.4 - 6.1. Because acidic substances can corrode metals (such as this iron spoon) it is feared that metal components can be mixed in honey. Like the concept of cooking utensils with acidic ingredients too. Not all honey has the same level of acidity.
Rhomboid Protease Enzyme Photograph by Laguna Design Pixels
Enzymes Without a doubt, heating and filtering honey reduces the final quantity of enzymes in honey. Enzyme levels dropped an average of about 35% when heating and DE filtration was used. Enzyme levels dropped about 15% using heating and straining. Enzymes such as invertase were nearly completely eliminated by processing (average drop of 73%.