Mead Lovers Between beer and mead, behold braggot

The Difference Between a Craft Beer and a Micro Brew Beer Craft beer
Mead is not considered a style of beer, since the sugars in mead come from honey, not from the starch of a grain. Hops are sometimes added to mead for flavor and as a preservative. The process for making mead is more similar to wine making than brewing beer. There's no brewing (boiling) stage necessary in making mead.

Mead vs. Ale The Differences Between Ale and Mead
Some use no heat whatsoever. But ultimately, while mead can be made from any honey, raw honey is where the drink really shines. The natural enzymes, compounds, and even wild yeasts play vital roles to the flavor profile of the finished mead. But while the "raw-ness" of the honey determines its complexity, time might play an even bigger role.
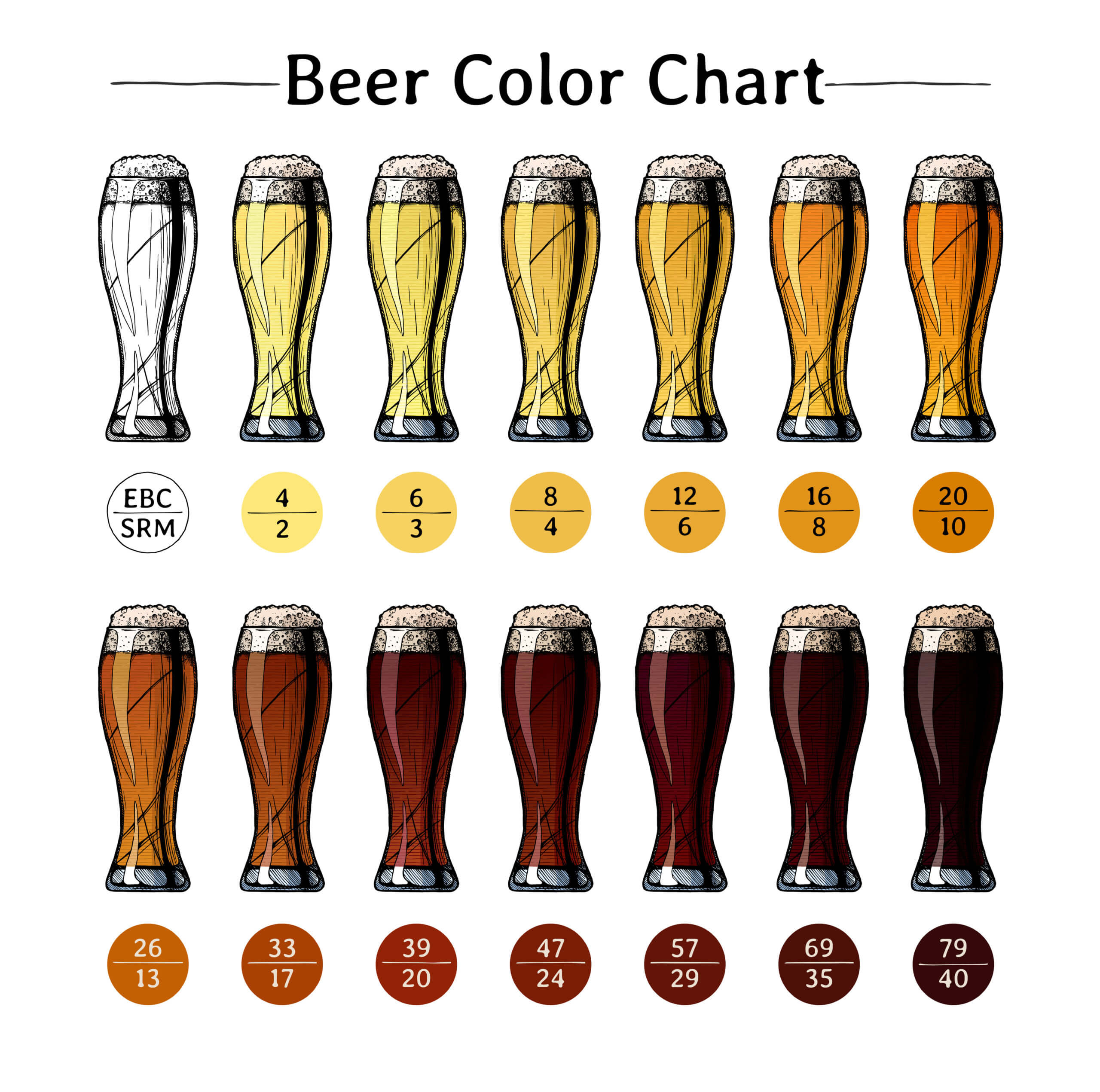
How are Brown Ales Different from a Porter or Stout?
One of the main differences between mead, beer, and wine is the basic ingredients used to make each, especially the source of the sugar that is fermented to create alcohol. Beer is made by fermenting sugars drawn from grains. Wine is made from fermenting grape juice. Mead is made from fermenting a mix of honey and water.

Mead vs. Ale The Differences Between Ale and Mead
Mead has a fruity and winey flavor, whereas beer — whether ale or lager — has a more malty flavor. Beer has crisp, hoppy, malty, or roasted in terms of taste. The magical combination of malt hops and yeast is typically responsible for a beer's characteristic flavors.

Marvellous Mead A Guide To Mead Drinks & More
Mead vs Beer Taste. The most noticeable difference between mead and beer is the taste. Mead has a sweet, honey-like flavor, while beer can have a range of flavors from malty and sweet to hoppy and bitter. The type of beer you choose will also affect the flavor, with some beers having a light taste while others are stronger and full-bodied.

Beer vs Mead What's The Difference?
The main differences in the production of a sweet mead and a dry mead all comes down to using the right type of yeast. Mead has it's own vocabulary for alcohol content as well. Hydromel mead has the lowest alcohol content of 3.5 - 7.5%, session meads have an alcohol content of almost 6.5%, while sack meads are more in the range of 14 - 18%.

Discover the Difference Between Mead and Beer
Yeah, no. Mead has beer properties, but it's not beer, kind of the same way true mead is kind of a wine but not. Mead is just mead. The main similarity between mead and beer is that both have a broad set up subcategories amid more prevalent styles—think lager, ale, and stout. Both craft beers and craft mead have incredible versatility.

Mead vs. Beer What's The Difference?
What is the Difference Between Mead and Beer? Mead and beer are both types of alcoholic beverages that are thousands of years old, but they are made using very different ingredients. Mead is traditionally made from honey, while beer is made from malted barley and hops. Mead may also contain spices or fruits, while beer traditionally does not.

Mead Lovers Between beer and mead, behold braggot
The final, and by far biggest, difference between mead and beer is the alcohol content of each drink. Most beers in the US will settle around the 5 - 6% alcohol by volume (ABV) range, although some New York artisanal beers can often go as high as 10 -12 % ABV. Mead has a much wider ABV range with different varieties ranging from as low as 3%.

Mead vs Beer Let’s Settle the Debate Once and for All
The main difference between mead and beer is the primary fermentable ingredient used in the brewing process. Mead is made from fermented honey and water, while beer is made from fermented grains and water. This difference in ingredients also means that mead and beer have different flavor profiles, aromas, and textures.

The Real Difference Between Root Beer And Birch Beer
1. Mead is a fermented beverage made from honey, water, and yeast. 2. The quality and quantity of honey used can greatly impact the mead's flavor and alcohol content. 3. Cyser is a type of mead that combines honey and apple juice or cider. 4. The type of apples used in Cyser can alter its taste significantly. 5.

What’s the Difference Between Mead, Cyser, Braggot & Melomel? — Viking
Another difference between meads and beers is their bases. The base of a mead is diluted honey. As we have said above, this base is called a must. On the other hand, the base of a beer is the solution from the mashing step. This base is called the wort.

What Is the Difference Between Beer Yeast and Wine Yeast?
Top Things to Know About Mead vs. Beer: Mead is an alcoholic beverage made from fermenting honey while beer is made fermenting hops and malt (grains) Mead is made largely from honey, and beer is made from grains. Mead is gluten-free, whereas beer is not gluten-free Mead takes longer to ferment than beer, typically a few months to a few years versus a few weeks to a few months. Mead is not mead.

The Difference Between Beer and Wine Beer vs Wine
Conclusion. In conclusion, ale and mead beers are two distinct types of beer with different origins, ingredients, fermentation processes, flavor profiles, and mouthfeel. Ale is typically a darker-colored beer with more bitterness than mead due to its higher alcohol content. On the other hand, mead is lighter in color with less bitterness and.

Food history the difference between mead and beer Norway
Mead is primarily crafted from honey, while beer is made from malted barley. Beer contains hops that introduce bitterness to balance the sweetness from the wort, while mead does not have hops. Mead has a wide range of alcohol content, ranging from 7% to 20%ABV, while most beers have an alcohol range of 3.5% to 10% ABV.
Mead vs. Beer Is There a Difference? Batch Mead
Let's first take a look at where both mead and beer got their starts. Introduction to Mead's History. Mead, often revered as the ancestor of all fermented drinks, boasts a history that traverses the globe, predating known history.This honey-based alcohol has been discovered in cultures across Europe, Asia, and Africa, with evidence suggesting its consumption thousands of years ago.