Spinal Cord Anatomy Parts and Spinal Cord Functions
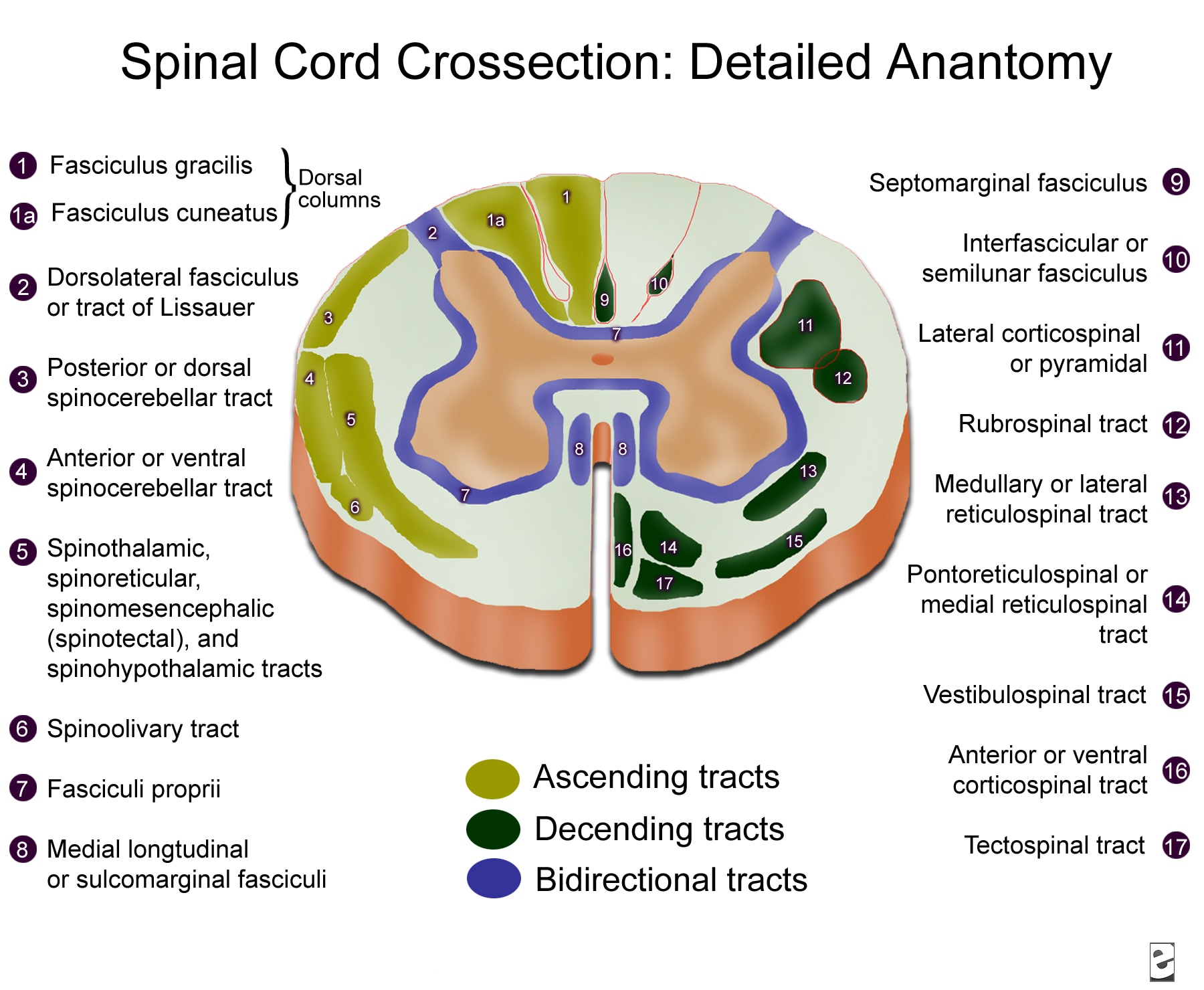
Spinal Cord Cross sectional Anatomy rdiOlogY dE aruN
Internal and external anatomy, blood supply, meninges. In cross-section studies, the spinal cord has a narrow channel in its middle called the central canal.It is filled with cerebrospinal fluid and is continuous with the fourth ventricle of the brain.
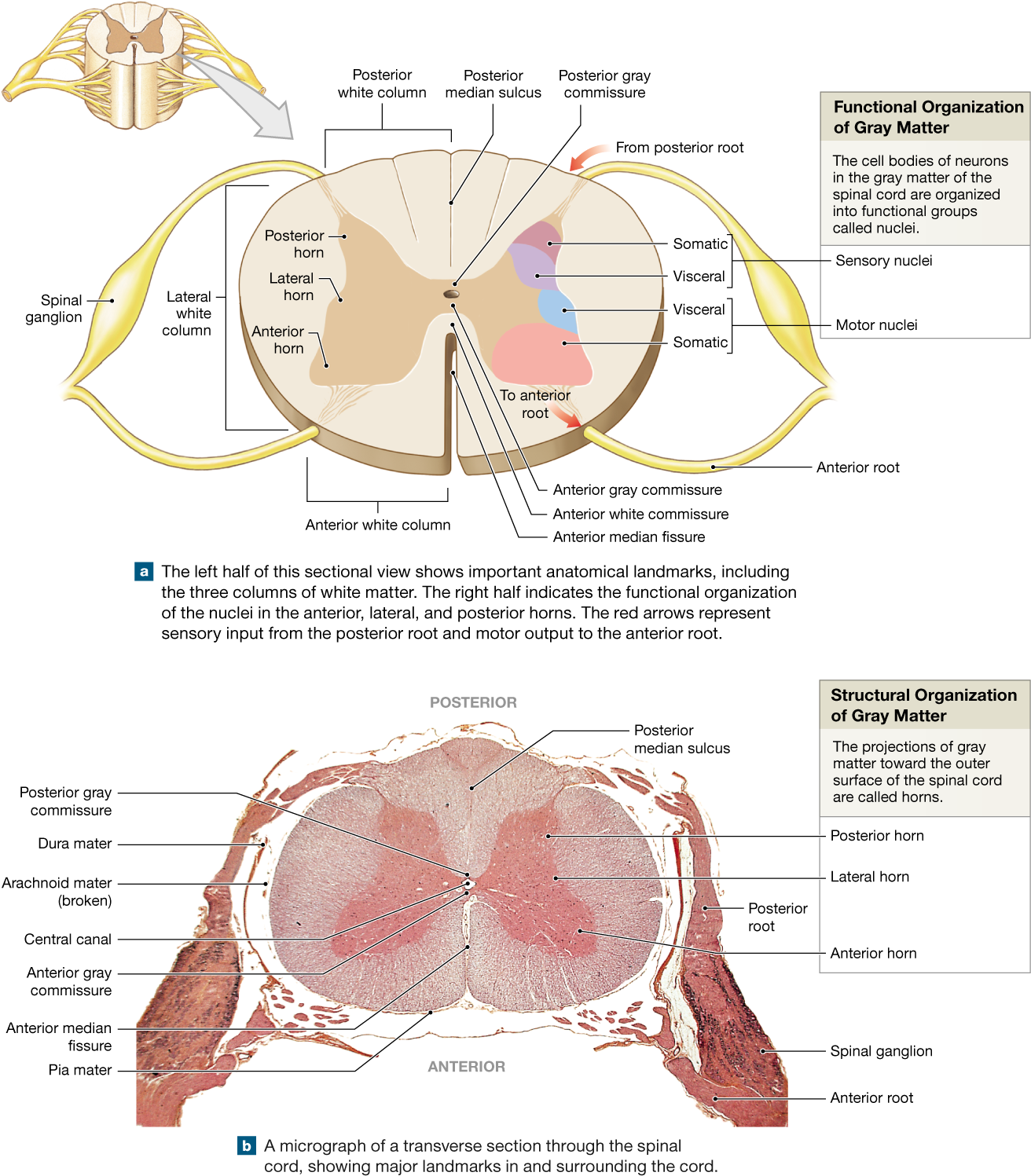
Download Spinal Cord Gray Matter Integrates Information And Label
Spinal Cord Sectional Anatomy. Animation in the reference. Diagrams of the spinal cord. Cross-section through the spinal cord at the mid-thoracic level. Cross-sections of the spinal cord at varying levels. Cervical vertebra. A portion of the spinal cord, showing its right lateral surface. The dura is opened and arranged to show the nerve roots.

14.4 The Spinal Cord Anatomy & Physiology
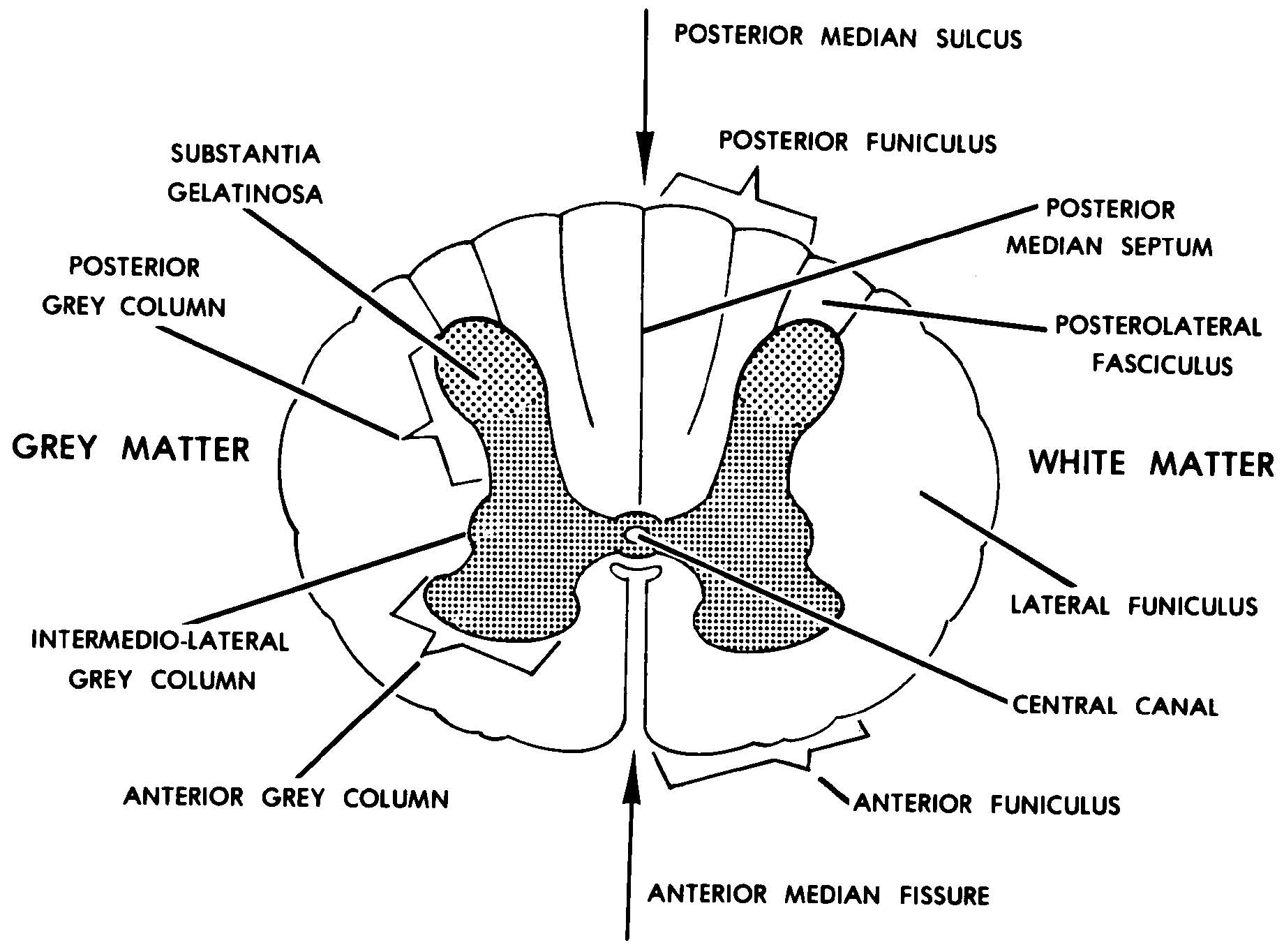
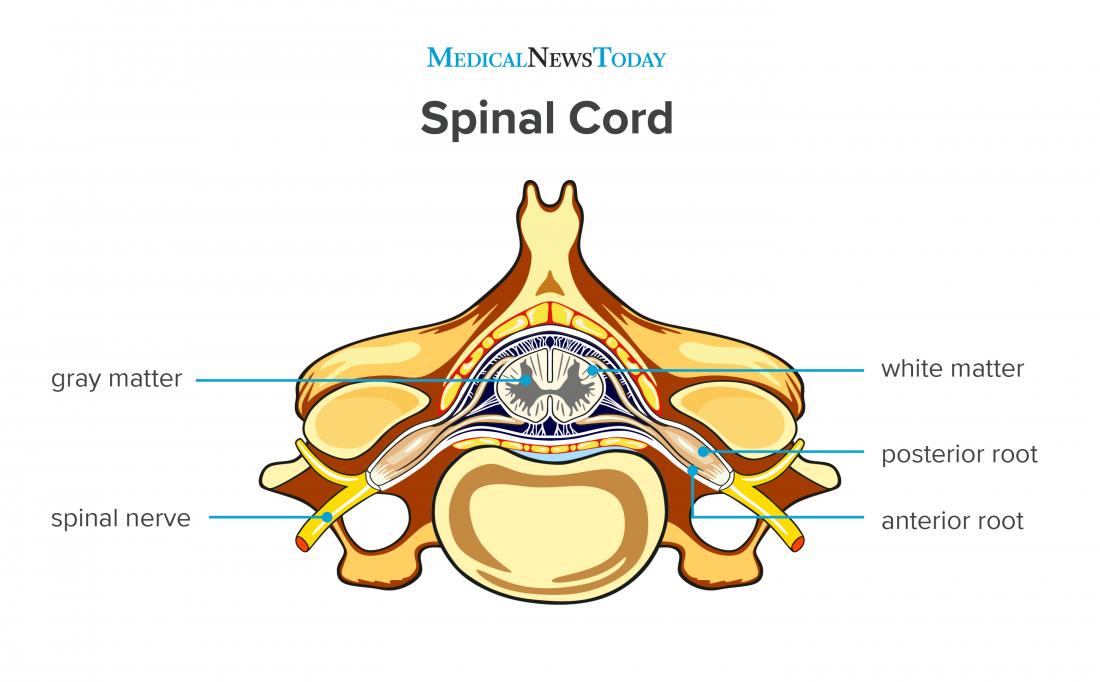
Cross Section Anatomy of the Spinal Cord. Like the brain, the spinal cord is also made up of regions of white matter and gray matter. White matter regions are comprised of axons. It appears white due to the myelin sheath on the axons. Gray matter regions are comprised of cell bodies and dendrites. Gray matter is the location of most synapses.
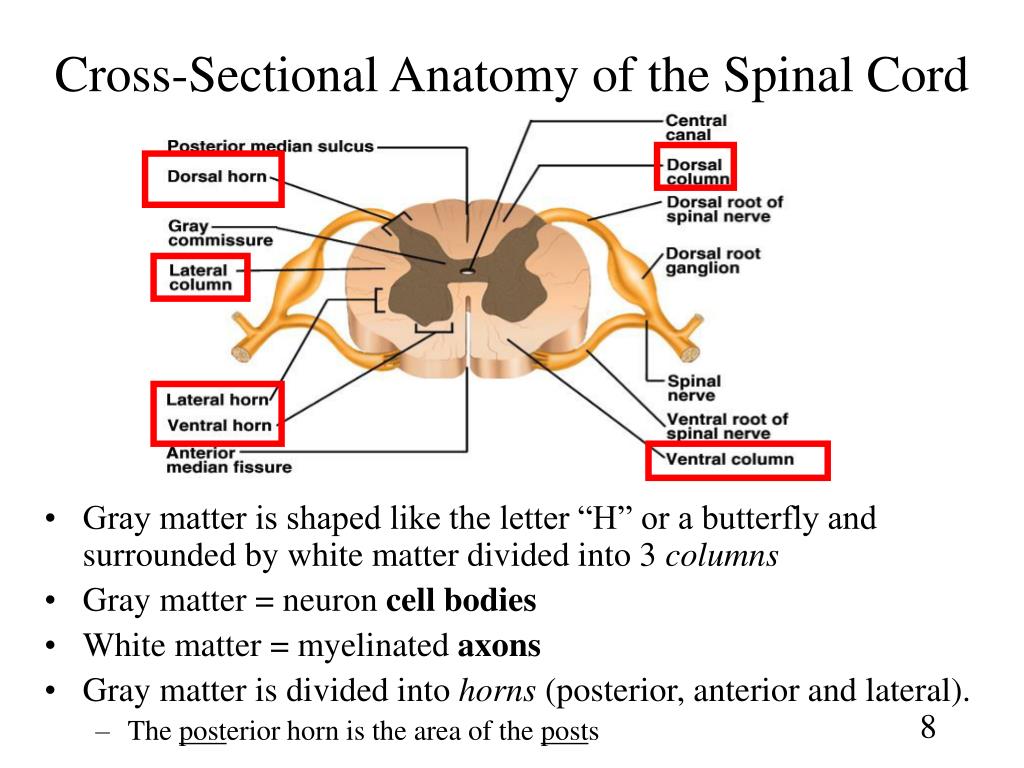
PPT Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Nerves and Reflexes PowerPoint
Spinal Cord Segments - Cross-sectional Anatomy. The spinal cord is made up of 31 segments, this tutorial shows some anatomy, cross section and histology images of the segments in interactive way. Skeletal muscle fibers: arrangement and location > External Intercostal Muscles.

Spinal Cord Anatomy Parts and Spinal Cord Functions
Cross-sections of the Spinal Cord Create healthcare diagrams like this example called Cross-sections of the Spinal Cord in minutes with SmartDraw. SmartDraw includes 1000s of professional healthcare and anatomy chart templates that you can modify and make your own.

Spinal Cord Picture Anatomy koibana.info Spinal nerves anatomy
Take a look at the spinal cord cross section diagram below. Here you can see the white and gray matter of the spinal cord and the associated structures such as funiculi, lamina and tracts. Thinking of the information you learned in the video, spend some time linking the location of the labeled structures with what you know about their function.

CrossSectional Anatomy of the Spinal Cord. (a) Relationships to the
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system and consists of a tightly packed column of nerve tissue that extends downwards from the brainstem through the central column of the spine. It is a relatively small bundle of tissue (weighing 35g and just about 1cm in diameter) but is crucial in facilitating our daily activities.. The spinal cord carries nerve signals from the brain to other.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1900/4wg7EtKVwtWY7wcLa4OtAA_anatomy-spinal-cord-cross-section_english.jpg)
Ascending tracts of the spinal cord Anatomy Kenhub
Spinal Cord Cross Section Labeling — Quiz Information This is an online quiz called Spinal Cord Cross Section Labeling You can use it as Spinal Cord Cross Section Labeling practice, completely free to play.
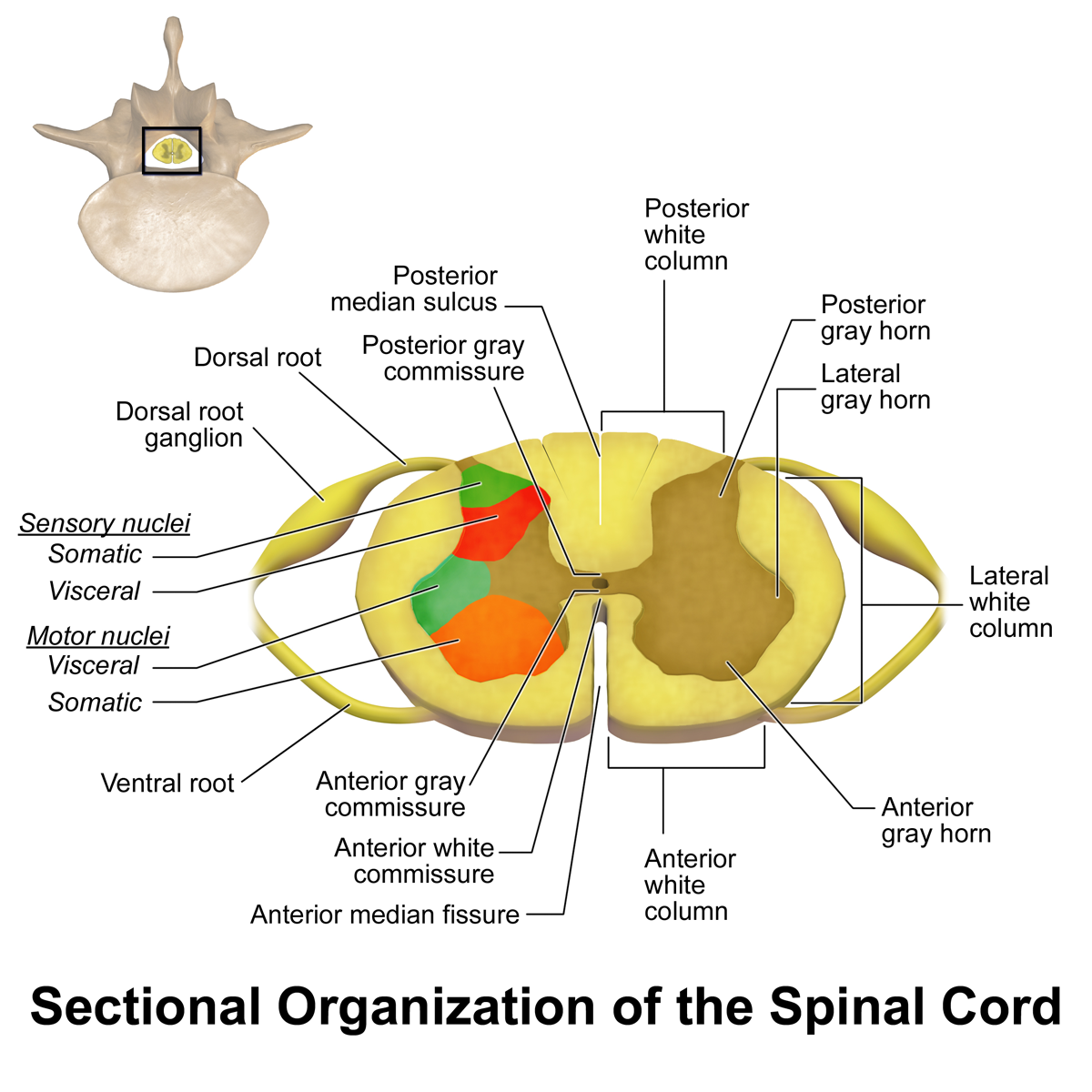
Spinal Cord Summary Neuroanatomy Geeky Medics
Spinal Cord Segments - Cross-sectional Anatomy. The spinal cord is made up of 31 segments. Each segment gives rise to a pair of spinal nerves. In cross-section (c.s.), the segments appear to be divided into two zones. The outer zone contains many myelinated axons that run up and down the spinal cord.
Images 11. Nervous System Basic Human Anatomy
The vertebra provides several crucial functions to the body. First, it acts as a structural component of the spine, bearing body weight, anchoring muscles and the spinal cord, and forming joints with other vertebrae and ribs that allow the torso and neck to move. Second, the vertebra protects the delicate tissues of the spinal cord by.

SpinalCordCrossSectionTractsimageVbKM.jpg 1,347×1,600 pixels
Internal anatomy of the spinal cord. The following discussion of the internal anatomy of the spinal cord will introduce some of the general principles of organization that also hold true for the brainstem. A cross-section through the spinal cord is illustrated schematically in Figure 2.6 and 3.4. The gray matter forms the interior of the spinal.

Table 1 and 2, Gross Anatomy and Cross Section of the Spinal Cord
Next, the user will find anatomical sections of the spinal cord at different levels: cervical spinal cord (C2, C5), thoracic spinal cord (T10), lumbar spinal cord (L3) and sacral spinal cord (S3). Anatomy : Spinal cord, Funiculi of spinal cord, Tectospinal tract, Anterior funiculus; Ventral funiculus, Cuneate fasciculus, Gracile fasciculus.

Spinal Cord Anatomy Parts and Spinal Cord Functions
Spinal Cord Anatomy. formed by S2, S3, S4 parasympathetic fibers and lumbar sympathetic fibers (splanchnic nerves) is residual fragment of spinal cord that extends from conus medullaris to sacrum. the dural surrounded sac that extends from the spinal cord and contains CSF, nerve roots and the cauda equina.
Spinal cord Anatomy, functions, and injuries
Gross anatomy. The spinal cord measures approximately 42-45 cm in length, ~1 cm in diameter and 35 g in weight. Like the brain, it is composed of grey and white matter.However, unlike the brain, the grey matter is on the internal aspect of the cord, and the white matter tracts are external. Throughout its length, paired dorsal and ventral nerve roots enter its dorsolateral and ventrolateral.

Spinal Cord Cross Section Labeled Spinal Cord Anatomy Structure
Looking at the spinal cord cross-section, the top wings of the gray matter "butterfly" reach toward the spinal bones. The bottom wings are toward the front of the body and its internal organs.

Pin on Biology
Overview of spinal cord anatomy The spinal cord is a cylindrical mass of neural tissue extending from the caudal aspect of the medulla oblongata of the brainstem to the level of the first lumbar vertebra (L1).While the length of the spinal cord varies from one individual to another, it is usually longer in males (approximately 45 cm) than it is in females (approximately 42 cm).