UNA MUCCA CHE RICICLA E CONSERVA

Stomaco anatomia, funzioni, patologie, cure e prevenzione Melarossa
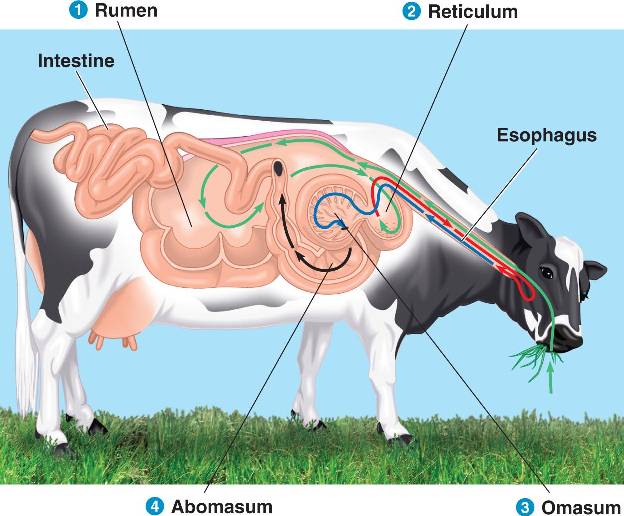
Tutti gli stomaci della mucca Il rumine. Il primo stomaco delle mucche è chiamato rumine. Questo è il più grande dei quattro stomaci e può contenere fino a 50-60 litri di cibo. Il rumine è una sorta di sacco di fermentazione, dove il cibo viene immagazzinato temporaneamente prima di essere digerito. Qui, i batteri e altri microrganismi.

Quanti stomaci ha una mucca?
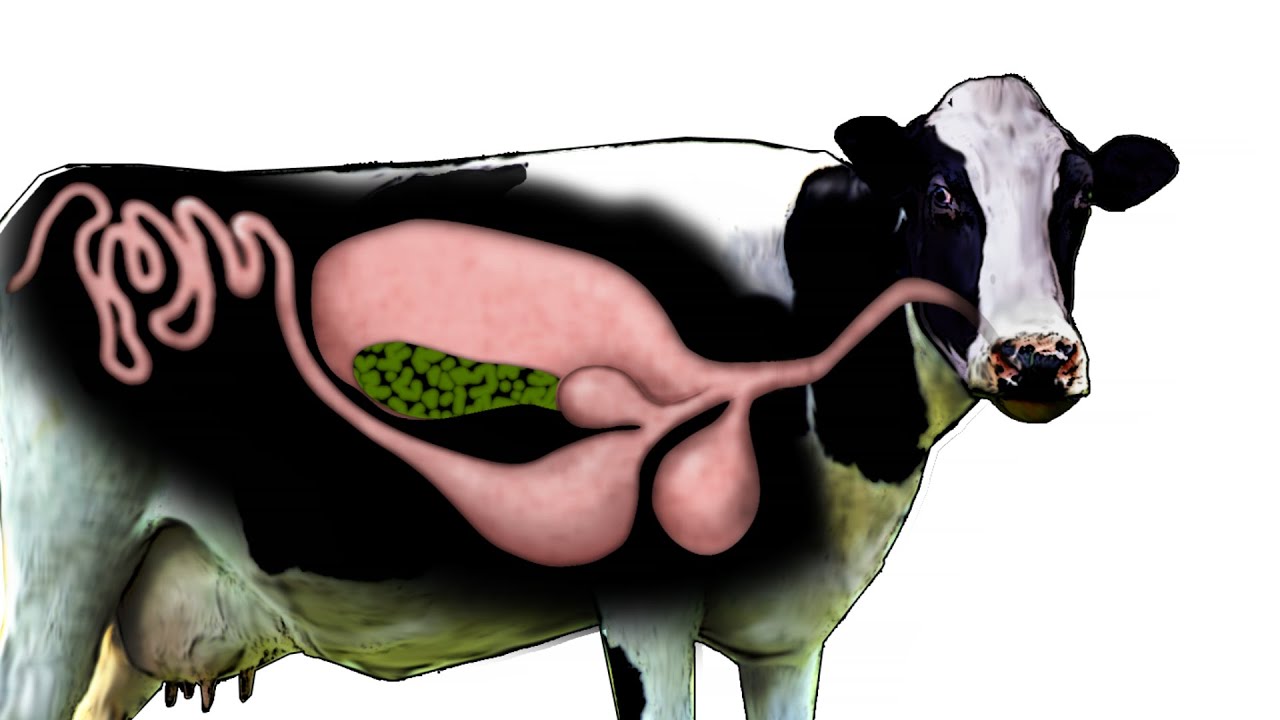
Popolarmente si sente dire che le mucche hanno 4 stomaci ma si tratta di una asserzione imprecisa e incorretta. Le mucche infatti sono fornite di un solo stomaco, che a sua volta è diviso in quattro camere o parti: il rumine, il reticolo, l'omaso e l'abomaso. In ciascuna di queste camere si svolge una fase del processo di digestione.
%2C_Liegende_Kuh_--_2011_--_1526.jpg/1200px-Flumserberg_(Schweiz)%2C_Liegende_Kuh_--_2011_--_1526.jpg)
mucca Wikizionario
Human digestive system - Gastric Mucosa, Digestive Processes, Enzymes: The inner surface of the stomach is lined by a mucous membrane known as the gastric mucosa. The mucosa is always covered by a layer of thick mucus that is secreted by tall columnar epithelial cells. Gastric mucus is a glycoprotein that serves two purposes: the lubrication of food masses in order to facilitate movement.

Stomaco della mucca fotografia stock. Immagine di intestini 35011256
L'apparato digerente della mucca: la mucca ha quattro stomaci. Una mucca può consumare in media 70 kg di erba al giorno per un periodo di 8 ore. È in grado di farlo grazie al suo speciale sistema anatomico e fisiologico che gestisce la digestione. Diamo un'occhiata al nostro strano stomaco.

Le mucche fistulate Butac Bufale Un Tanto Al Chilo
Erosive gastritis means the thing that's causing your gastritis is actually eating away at your stomach lining, leaving wounds (ulcers). It's often a chemical, like acid, bile, alcohol or drugs. Nonerosive gastritis doesn't leave erosive changes but may cause irritation, such as reddening of the stomach lining.
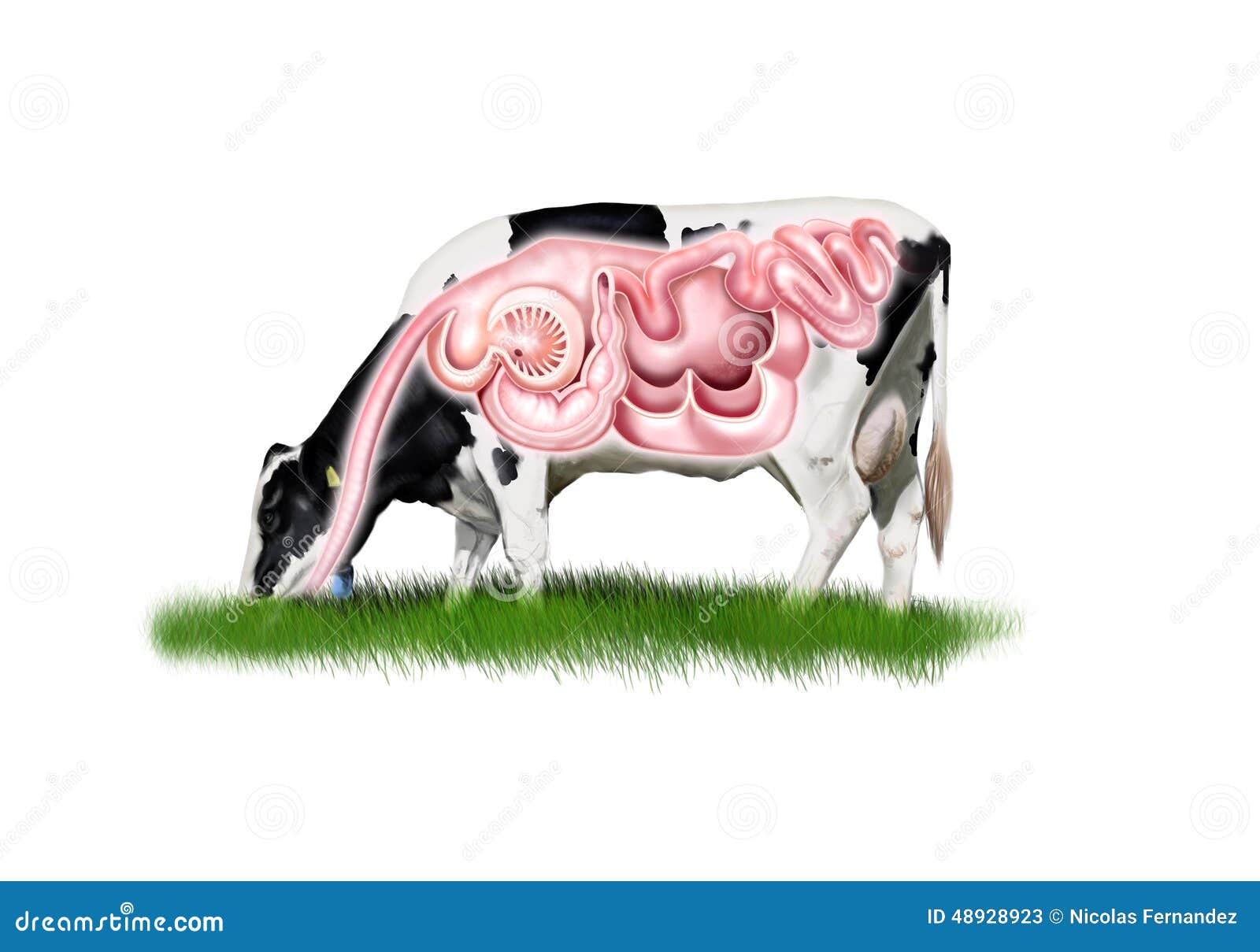

Cow digestive system stock illustration. Illustration of milk 48928923
I numerosi stomaci della mucca Forse non tutti sanno che la mucca, essendo un ruminante, ha quattro stomaci (quindi anche pecore e capre). In realtà si tratta di tre prestomaci di origine esofagea e di uno stomaco ghiandolare (come il nostro).

Stomaco Della Mucca Immagine Stock Libera da Diritti Immagine 35011256
The stomach is an important organ and the most dilated portion of the digestive system. The esophagus precedes it, and the small intestine follows. It is a large, muscular, and hollow organ allowing for a capacity to hold food. It is comprised of 4 main regions, the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus. The cardia is connected to the esophagus and is where the food first enters the stomach. The.
Raw Cow Stomach (Tripe) YouTube
Stomaco umano. Organizzazione generale della parete gastrica. Lo stomaco è la porzione più dilatata del canale alimentare. La sua parete risulta costituita dalla sovrapposizione della tonaca mucosa, della tonaca sottomucosa, della tonaca muscolare e della tonaca sierosa. L'epitelio di rivestimento della tonaca mucosa è batiprismatico.
A Plain and Simple Homeschool Science Week 13 Hoofs, Horns, Antlers
When they happen, symptoms might include indigestion and pain in the upper part of the belly. Symptoms might not happen until the cancer is advanced. Later stages of stomach cancer might cause symptoms such as feeling very tired, losing weight without trying, vomiting blood and having black stools.

UNA MUCCA CHE RICICLA E CONSERVA
The stomach is a key part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, sitting between the esophagus and duodenum.Its functions are to mix food with stomach acid and break food down into smaller particles using chemical and mechanical digestion. The stomach can perform these roles due to the layers of the stomach wall.These are the gastric mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa and serosa.

Gli Organi Interni Della Mucca Di Base Ed I Tagli Del Manzo Tracciano
Symptoms. The signs and symptoms of gastritis include: Gnawing or burning ache or pain (indigestion) in your upper abdomen that may become either worse or better with eating. Nausea. Vomiting. A feeling of fullness in your upper abdomen after eating. Gastritis doesn't always cause signs and symptoms.

Il Sistema Dello Stomaco Di Mucca Illustrazione Vettoriale
Muscularis mucosæ. m'. Muscular tissue within the mucous membrane. The gastric mucosa is the mucous membrane layer of the stomach, which contains the glands and the gastric pits. In humans, it is about 1 mm thick, and its surface is smooth, soft, and velvety. It consists of simple columnar epithelium, lamina propria, and the muscularis mucosae .

Quanti stomaci hanno le mucche? Caratteristiche e curiosità
These include gastrin, which is released mainly by enteroendocrine G cells. Table 23.4.1 23.4. 1 describes the digestive functions of important hormones secreted by the stomach. Watch this animation that depicts the structure of the stomach and how this structure functions in the initiation of protein digestion.

Trippa Cos'è e tipi di trippa Alimentipedia.it
Lo stomaco delle mucche. Una mucca non ha quattro stomaci, ne ha solo uno, diviso in quattro scomparti diversi: il rumine, il reticolo, l'omaso e l'abomaso. Ogni parte dello stomaco scompone il cibo per consentire al corpo di estrarre ogni nutriente. Mucche, pecore, capre, cervi, renne, bisonti, cammelli e persino antilopi hanno l.

Le mucche col buco L'abominevole pratica della fistulazione
I numerosi stomaci della mucca Forse non tutti sanno che la mucca, essendo un ruminante, ha quattro stomaci (quindi anche pecore e capre). In realtà si tratta di tre prestomaci di origine esofagea e di uno stomaco ghiandolare (come il nostro). Di conseguenza, quanti stomaci ha il toro? Apparato digerente Il bue domestico, essendo un ruminante.

Quanti stomaci ha una mucca? North American Nature Creative Saplings
I numerosi stomaci della mucca. Forse non tutti sanno che la mucca, essendo un ruminante, ha quattro stomaci (quindi anche pecore e capre). In realtà si tratta di tre prestomaci di origine esofagea e di uno stomaco ghiandolare (come il nostro).