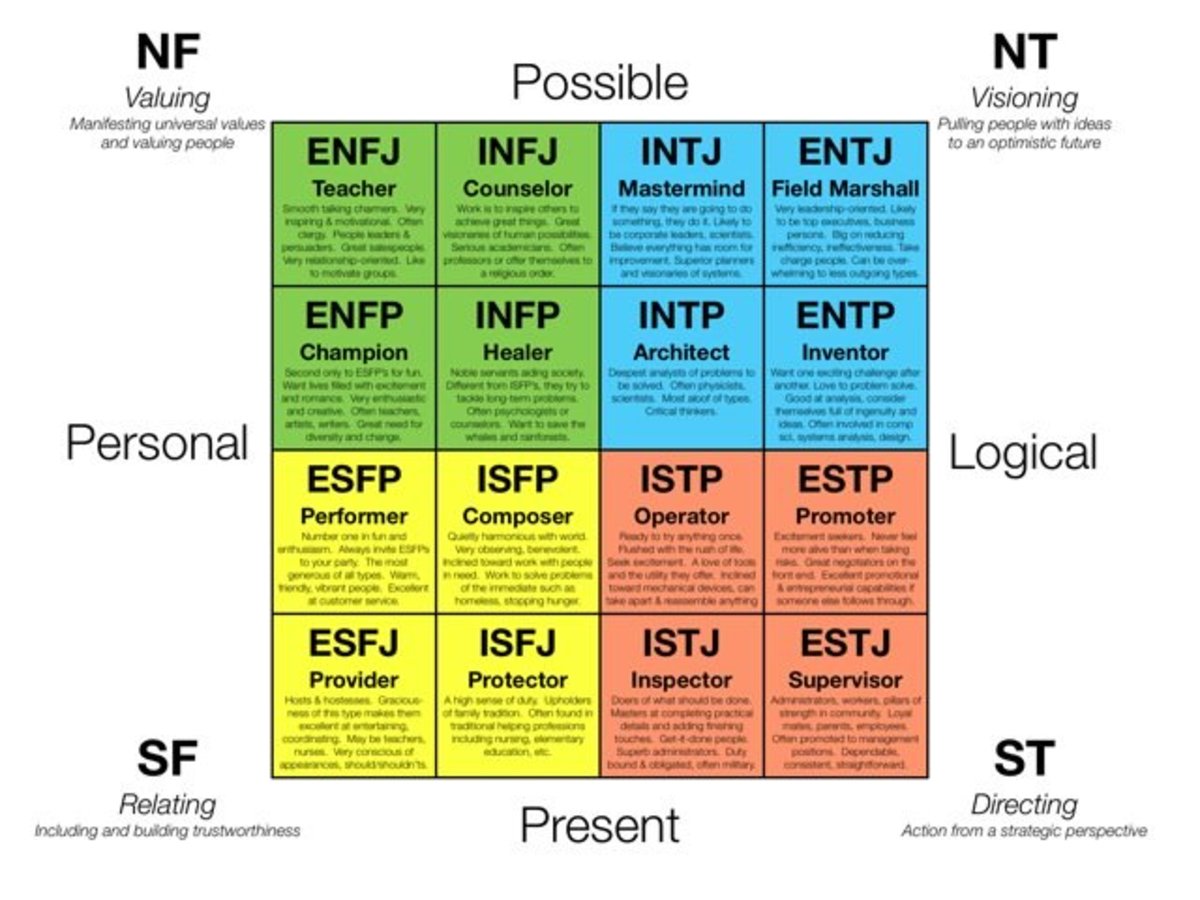
How the MyersBriggs Type Indicator Works 16 Personality Types

MeyersBriggs Classification Models by Alex S Analytics Vidhya Medium
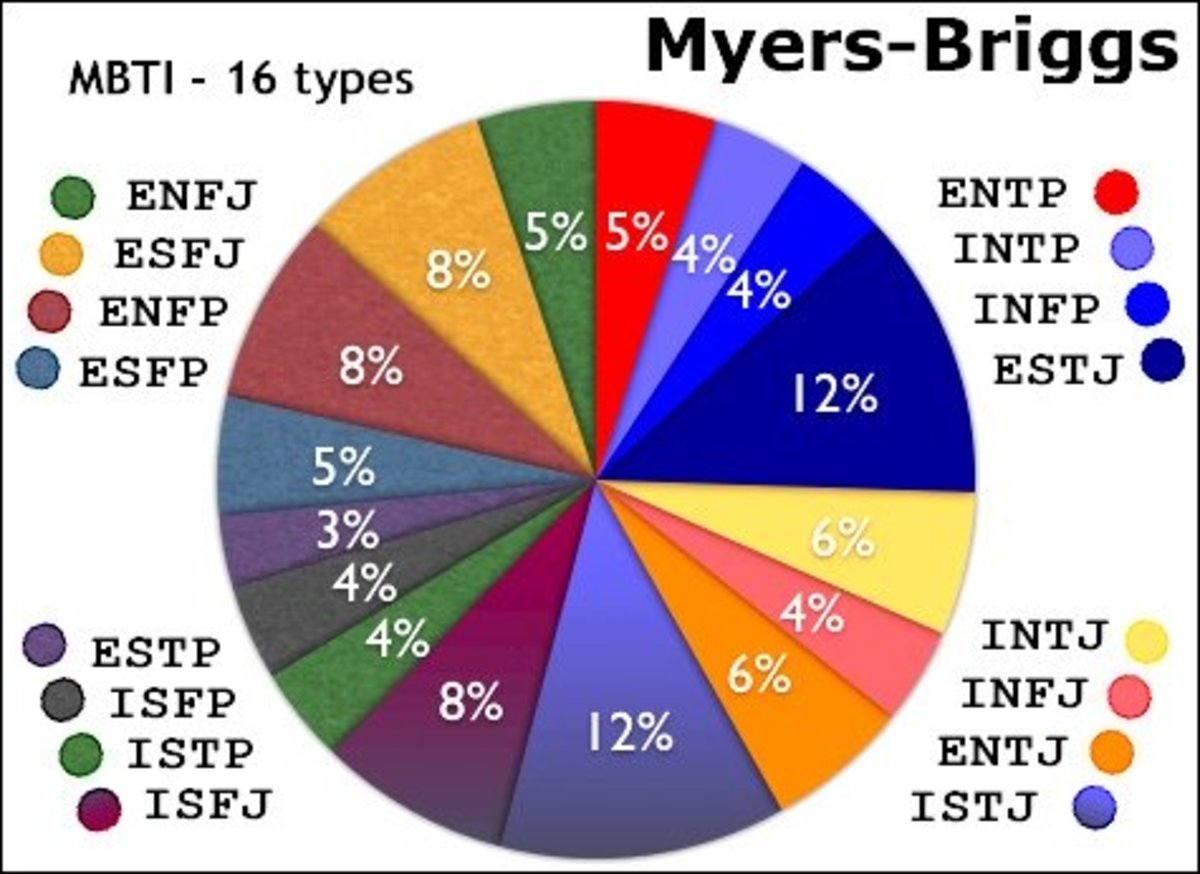
Myers-Briggs The 16 MBTI system and is the key to understanding type. Learn about process pairs and an overview of how type dynamics works. model is developmental. Discover the pathway for type development over the lifespan. assessment for helping you choose a career and manage career changes at every life stage.

MBTI explained Personality types chart, Myers briggs personality types, Personality chart
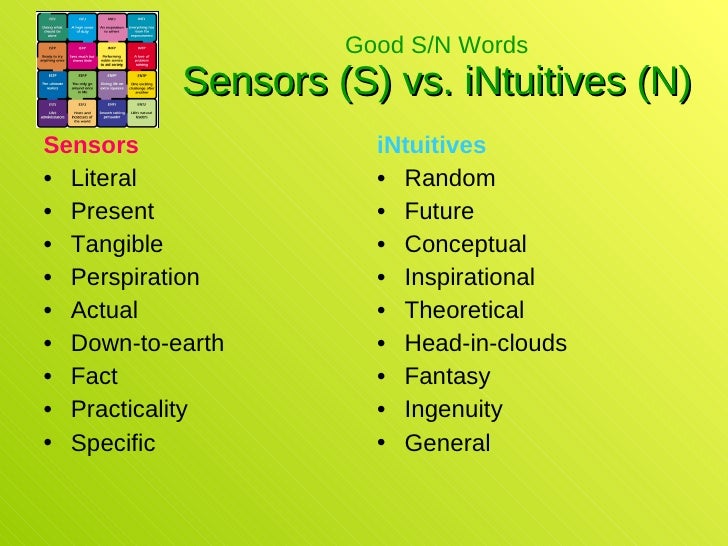
Core Theory Mind: Intuitive (N) vs. Observant (S) Thought at Every Scale Our second personality scale includes the Intuitive (N) and Observant (S) styles. These traits describe what people are more likely to do with the information gathered from the world around them.

How the MyersBriggs Type Indicator Works 16 Personality Types
Explaining the differences between Intuition and Sensing in the 16 Myers-Briggs Personality Types. These are the signs of intuition vs sensing. If you want t.
The History and Significance of the MyersBriggs Personality Test Owlcation
You use Sensing (S) and Intuition (N) to receive and process new information either by using your five senses or in more abstract ways. Sensing and Intuition are opposite preferences. A person's natural tendency toward one will be stronger than the other. There are by far more Sensing people in the population than Intuitives.

Myers Briggs Personality Test Let’s Explore Your Personality Type!
In Myers & Briggs' personality typing, the Sensing/Intuition dichotomy describes how a person takes in information, whether through sensory-based experiences or by intuitively recognizing factual patterns and connections. Find your type
MyersBriggs Basic Presentation
In personality typology, the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator ( MBTI) is an introspective self-report questionnaire indicating differing psychological preferences in how people perceive the world and make decisions. It enjoys popularity despite being widely regarded as pseudoscience by the scientific community.
Myers Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) Learning Styles by Tracy Atkinson Medium
Myers-Briggs Intuition (N) vs. Sensing (S) SHARE THIS PAGE: 64 Shares. About A.J. Drenth. A.J. is a four-time author and recognized authority on personality typology. He founded Personality Junkie® in 2009 which has since grown to see over 3 million annual visitors. His work has been referenced in numerous publications and he currently boasts.
FileMyersBriggsTypes.png Wikipedia
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is an assessment of personality based on questions about a person's preferences in four domains: focusing outward or inward; attending to sensory.

Absolute Truth. N vs. S MyersBrigg Personality, Mbti personality, Infp personality
The S vs. N dimension indicates how one identifies, interprets and relates to data, which in turn can influence transition behavior. Sensors tend to be detail-oriented and linear, valuing facts and historical precedents. Intuitors are more likely to interact with data in a less-structured way, often thinking about the future more creatively and.

Myers Briggs Type Indicator ® (MBTI) OEC² Solutions LLC OEC² Solutions LLC Consulting
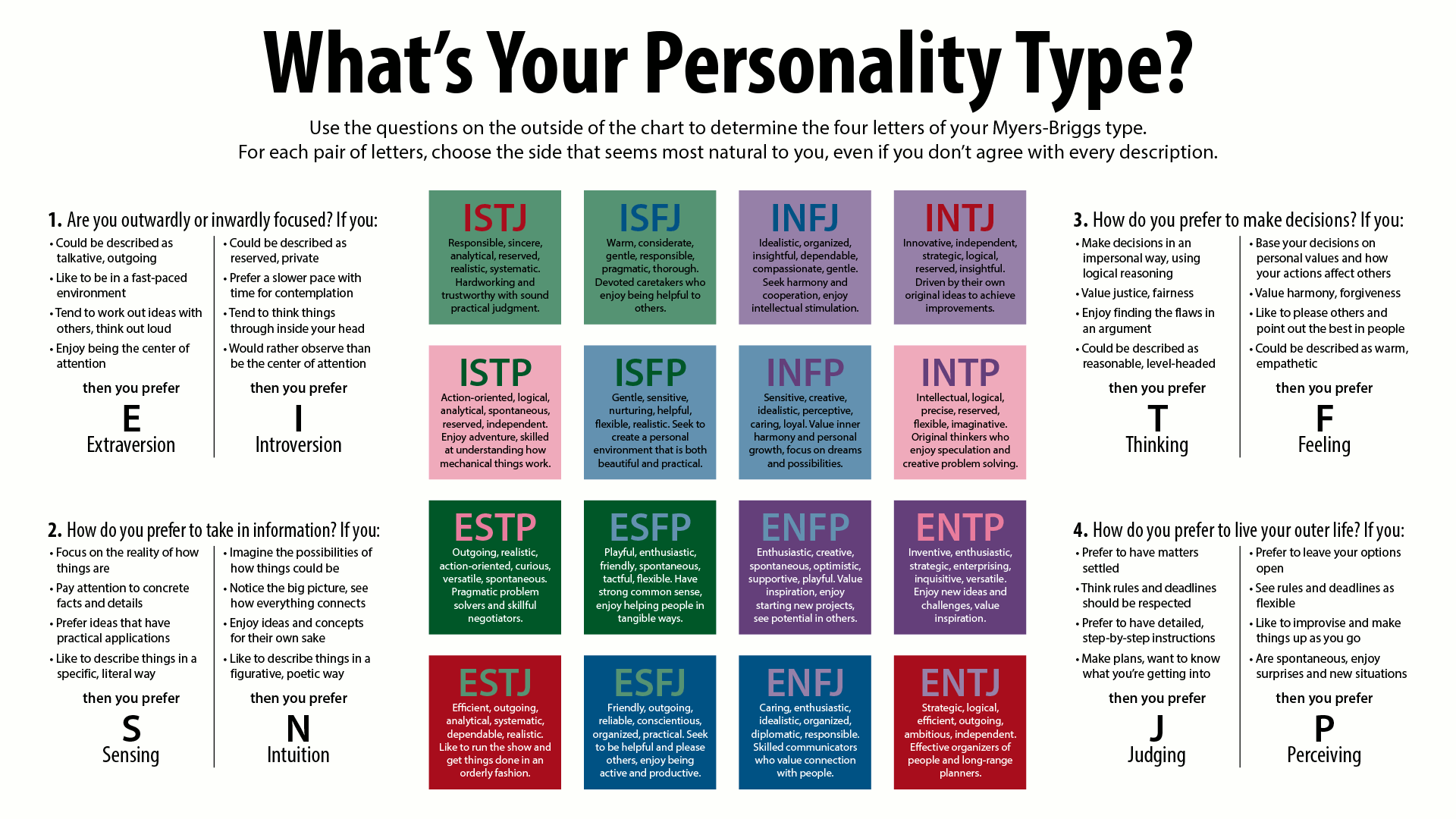
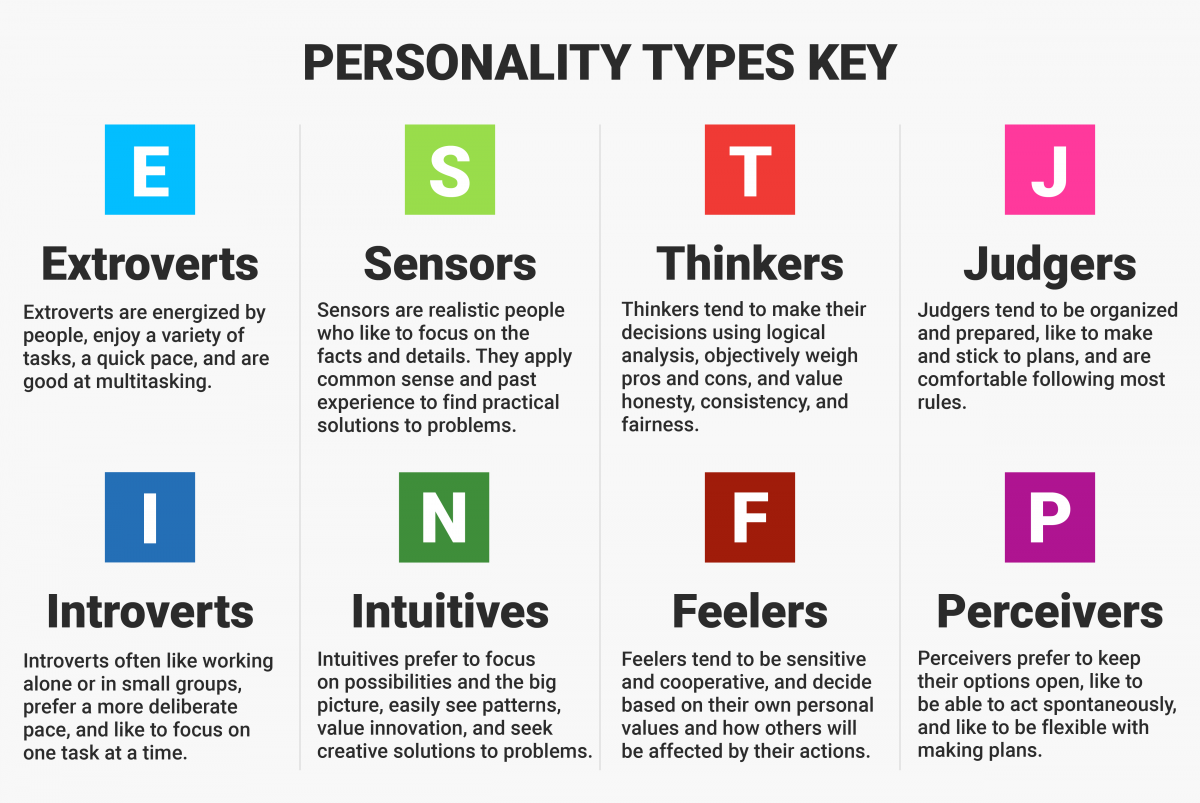
Created by renowned psychiatrist Carl Jung and popularized since the 1940s, the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) uses tailored questions to find your combination of four sets of opposing traits: introverted versus extroverted; sensing versus intuitive; thinking versus feeling; and perceiving versus judging.
MBTI Myers Briggs Type Indicator Shockingly Different Leadership
While there is some overlap between the Myers-Briggs and Big Five personality tests, the differences are apparent upon a closer examination. Personality types vs. personality traits. The primary difference between the Myers-Briggs and Big Five systems is that the latter does not identify you as belonging to a specific personality category.
History and Significance of the MyersBriggs Personality Test Owlcation
Myers-Briggs and Jungian Cognitive Functions . Introducing S vs. N. Thread starter Blackwater; Start. I've bolded what particularly fits me in the S and N descriptions and italicized what sort of fits, depending on the circumstances. S: Concrete Realistic Prize enjoyment Aware of current trends

MyersBriggs
Though there are many examples of S and N type personalities on the internet (where there are many debates on what is right or wrong) the general purpose is that in terms of the work you do, you enjoy processing information differently than your peers. One of my favorite examples is my partner-in-crime at Isagenix.

Pin by Kaye Smith on Personality types Personality types chart, Briggs personality test
One of the primary dichotomies in the Jungian personality taxonomy is intuition (N) vs. sensing (S). It is sometimes cast as a preference for the "big picture" (N) vs. details (S), theory (N) vs. practice (S), or abstract (N) vs. concrete (S) matters.

MyersBriggs Type Indicator (MBTI)
S is more interested in practical things (new or not), N is more interested in new things (practical or not). There's overlap, of course, in things that are both new and practical.

The MyersBriggs helps us understand different personality types ENTJA Life verses, Myers
October 3, 2023 Reviewed by Saul Mcleod, PhD On This Page: The Four Dichotomies The 16 Personality Types Benefits of MBTI Criticisms of MBTI The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is an introspective, self-report evaluation that identifies a person's personality type and psychological preferences.