
12 Ways to Support Students with ADHD Brookes Blog
ADHD is a disorder in which individuals have difficulty with executive functioning - an individual's decision-making ability, which involves working memory, inhibition of inappropriate or unhelpful responses, and ability to focus in on relevant information while dismissing unimportant or irrelevant information (Barkley, 2015).
Treatment ADHD NCBDDD CDC
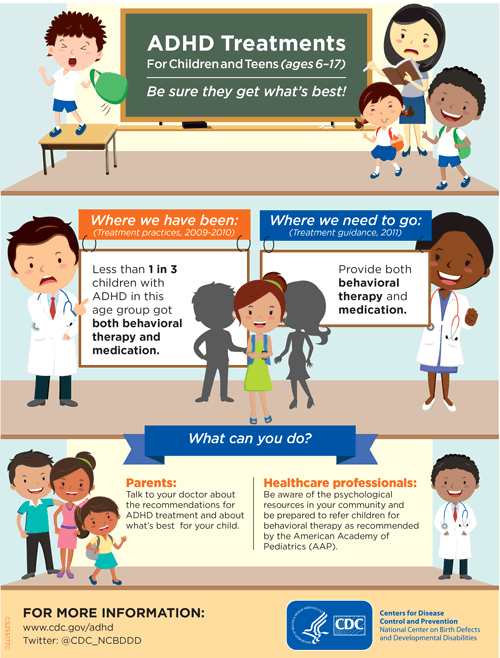
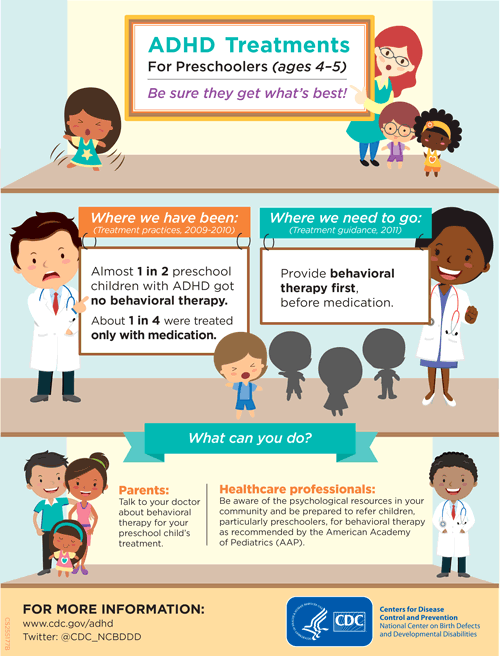
The symptoms of ADHD, such as inability to pay attention, difficulty sitting still, and difficulty controlling impulses, can make it hard for children with this diagnosis to do well in school. To meet the needs of children with ADHD, schools may offer. ADHD treatments, such as behavioral classroom management or organizational training;

Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children Harvard
ADHD is one of the most common neurobehavioral disorders of childhood. It is usually first diagnosed in childhood and often lasts into adulthood. Children with ADHD have trouble paying attention, controlling impulsive behaviors (may act without thinking about what the result will be), and in some cases, are overly active.

ADHD in Young Children VitalSigns CDC
Find activities to include students, especially younger ones, in helping out in the classroom. For children with ADHD, being a line leader, helping to pass out papers, and performing other helpful tasks can give them a sense of responsibility—which can boost their self-esteem. This can also be a great way to reduce issues that may otherwise.

25+ Strategies for Kids with ADHD The Pathway 2 Success
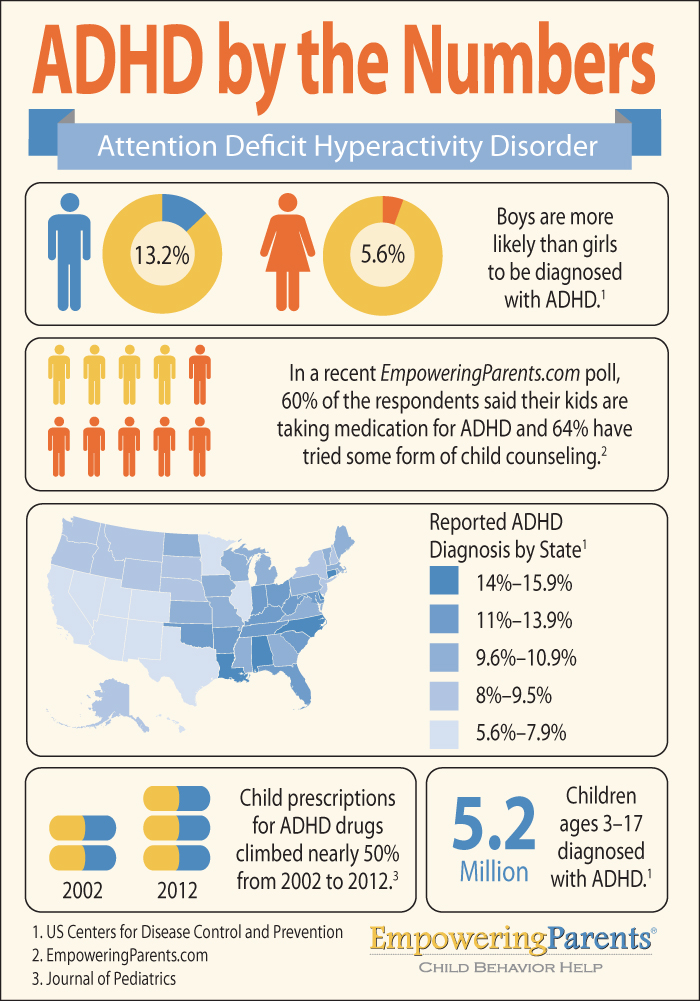
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC, 2017), a startling 11% of youth in the United States, between the ages of 4 and 17, have attention deficit hyperactivity. For students with ADHD, the classroom setting presents many challenges. Focusing attention and sitting quietly at a desk, skills often linked to academic.
Parent Training in Behavior Management for ADHD CDC
ADHD impacts each child's brain differently, so each case can look quite different in the classroom. Children with ADHD exhibit a range of symptoms: some seem to bounce off the walls, some daydream constantly, and others just can't seem to follow the rules.. CDC. (2019, November 7). ADHD in the Classroom. Centers for Disease Control and.
Guidelines ADHD NCBDDD CDC
Specific behavioral classroom management interventions and/or academic accommodations for children and teens have been shown to be effective for managing symptoms and improving functioning at school and with peers. Interventions may include behavior management plans or teaching organizational or study skills.. ADHD : CDC offers fact sheets.

Understanding ADHD Symptoms and Treatment by sanchit chaudhari Issuu
FDA-approved to treat ADHD in children as young as 6 years of age. : Stimulants are the best-known and most widely used ADHD medications. Between 70-80% of children with ADHD have fewer ADHD symptoms when taking these fast-acting medications. Nonstimulants were approved for the treatment of ADHD in 2003.
ADHD By The Numbers [Infographic]
Children and adolescents with ADHD typically benefit from classroom-based behavioral interventions and/or academic accommodations. Interventions may include behavior management plans or teaching organizational or study skills. Accommodations may include preferential seating in the classroom, reduced classwork load, or extended time on tests and.

Classroom Interventions and Modifications for Students with ADHD Free
The estimated number of children aged 3-17 years ever diagnosed with ADHD, according to a national survey of parents, 1 is 6 million (9.8%) using data from 2016-2019. This number includes. 12-17 years: 3.3 million (13%). ADHD diagnosis among children aged 3-17 years: State estimates vary from 6% to 16%. Learn about ADHD diagnosis and.

ADHD Approaching ADHD the Functional Medicine way
An interactive training taught by classroom teachers for classroom teachers, identifies common ADHD-related learning problems plus practical classroom techniques, interventions and the latest research to enhance school success for students with ADHD. Professional education credits are available for this training.

Recognizing ADHD in the classroomstrategy card for teachers
Symptoms. The primary features of ADHD include inattention and hyperactive-impulsive behavior.ADHD symptoms start before age 12, and in some children, they're noticeable as early as 3 years of age.ADHD symptoms can be mild, moderate or severe, and they may continue into adulthood.. ADHD occurs more often in males than in females, and behaviors can be different in boys and girls.

Fast Facts about ADHD
ADHD is one of the most common neurobehavioral disorders of childhood. It is usually first diagnosed in childhood and often lasts into adulthood. Children with ADHD have trouble paying attention, controlling impulsive behaviors (may act without thinking about what the result will be), and in some cases, are overly active.

25 strategies for kids with adhd Artofit
Listen quietly. Pay attention. Follow instructions. Concentrate. These are the very things kids with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD or ADD) have a hard time doing—not because they aren't willing, but because their brains won't let them. That doesn't make teaching them any easier, of course.

ADHD in the Classroom From a Mother's Point of View Breaking the
Modafinil (US Food and Drug Administration [FDA]-approved to treat narcolepsy and sleep apnea but not ADHD) in each individual study significantly improved ADHD symptoms, but aggregated estimates were nonsignificant (SMD, −0.76; CI, −1.75 to 0.23; studies = 4; n = 667) (Fig 2, Supplemental Table 1) because of high heterogeneity (I 2 = 91%).

Managing ADHD in the Classroom Effective Teaching Strategies
People with ADHD experience an ongoing pattern of the following types of symptoms: Inattention—having dificulty paying attention. Hyperactivity—having too much energy or moving and talking too much. Impulsivity—acting without thinking or having dificulty with self-control. Some people with ADHD mainly have symptoms of inattention.